Friday, December 27, 2024
Implementing the EDI 810 (Invoice) document in SPS Commerce
Implementing the EDI 810 (Invoice) document in SPS Commerce involves configuring the tool to map, transmit, and validate the EDI data according to trading partner requirements. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
---
### **Step 1: Gather Requirements**
1. **Understand Trading Partner Specifications**: Obtain the 810 EDI Implementation Guide (specifications) from your trading partner.
- Identify required segments, elements, and codes.
- Understand any validation rules or business-specific requirements.
2. **Define Business Rules**: Work with internal teams to outline the invoicing data flow and confirm all necessary data points are captured.
---
### **Step 2: Configure SPS Commerce Tool**
1. **Log in to SPS Commerce Fulfillment**:
- Access the web portal or integration tool provided by SPS Commerce.
- Ensure you have administrative privileges to configure document settings.
2. **Set Up Trading Partner Connection**:
- Navigate to the "Connections" or "Trading Partner Setup" section.
- Add or update the trading partner's profile to enable the 810 document type.
3. **Enable EDI 810 Document**:
- Locate the document setup menu for the trading partner.
- Select "810 Invoice" and ensure it is enabled.
4. **Map Data Fields**:
- Use SPS Commerce’s mapping tools to map your internal data (ERP or accounting system) to the 810 format.
- Map mandatory segments like **ST (Transaction Set Header)**, **BIG (Beginning Segment for Invoice)**, **N1 (Name)**, **IT1 (Invoice Line Items)**, and **TDS (Total Monetary Value Summary)**.
5. **Validate Mapping**:
- Perform test mapping for various scenarios (e.g., single item, multiple items, taxes, discounts).
- Ensure all required segments are mapped and optional ones are handled based on trading partner preferences.
---
### **Step 3: Test the Implementation**
1. **Generate a Test Invoice**:
- Create a sample invoice in your internal system.
- Export it to SPS Commerce.
2. **Run Mapping Validation**:
- Verify the data is translated into the correct EDI 810 format.
- Check the structure, syntax, and compliance with the trading partner’s specifications.
3. **Send Test EDI File**:
- Use the testing environment provided by SPS Commerce to transmit the 810 document to your trading partner. - Work with the trading partner to validate and troubleshoot any issues.
---
### **Step 4: Go Live**
1. **Confirm Trading Partner Approval**:
- After successful testing, obtain trading partner approval to go live.
2. **Enable Production Mode**:
- Switch the EDI 810 configuration from the test environment to production.
3. **Monitor Initial Transactions**:
- Closely monitor the first few live transactions for errors or discrepancies.
- Use SPS Commerce’s monitoring tools for error alerts and transaction tracking.
---
### **Step 5: Maintain and Update**
1. **Periodic Reviews**:
- Regularly review and update mappings to accommodate any trading partner updates or internal system changes.
2. **Error Resolution**:
- Use SPS Commerce’s error handling tools to address failed transactions.
- Work with support if needed.
3. **Expand Functionality**:
- As needed, implement additional documents (e.g., 850, 856) to enhance integration with your trading partner.
---
### Tools & Resources
- **SPS Commerce Documentation**: Reference guides and tutorials.
- **EDI Validator**: To check compliance.
- **Support Team**: Contact SPS Commerce for assistance during setup or troubleshooting.
Would you like detailed examples of specific 810 segments or mapping logic?
Sunday, November 17, 2024
Generate your trusted CRT , PEM and P12 security certificates for signing and encryption functionality for HTTP or HTTPS Communication
Monday, October 14, 2024
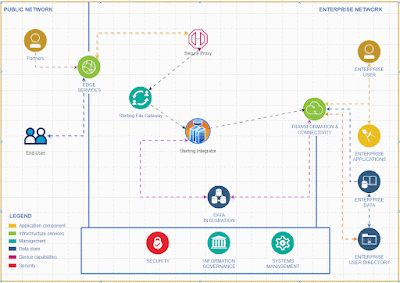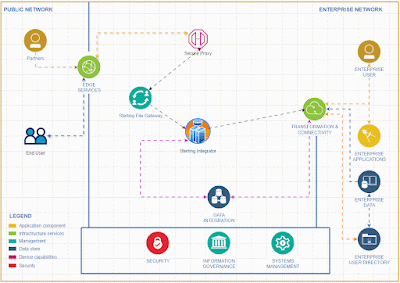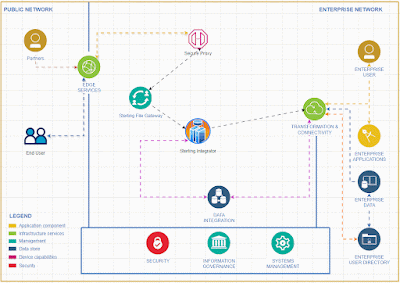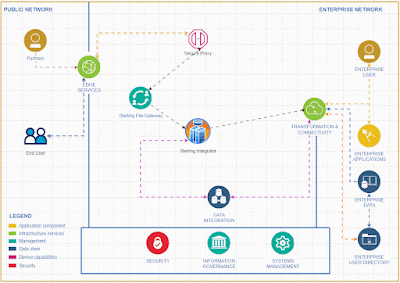
Introducing a rate limiter feature in IBM Sterling Integrator allows for comprehensive API functionality without the need to invest in additional API tools.
To activate and integrate the rate limiter feature in Sterling Integrator for comprehensive API functionality, follow these steps.To effectively deliver a service, it's essential to create a system that accepts input from clients and returns the appropriate output based on that input.
When we offer this service, it's important to pinpoint the client's IP address for any requests originating from outside our network.
To achieve the capability of identifying the client IP address within Sterling Integrator, we should adhere to the following steps.
To activate the Client IP feature, follow these steps: First, include the property client_ip_correlation_enabled=false in the jdbc.properties_platform_ifcbase_ext.in file.
Next, execute ./setupfiles.sh.
This feature captures the IP address of the client that initiates the request.
Certain clients require this functionality to comply with regulatory standards.
Before you enable the Client IP feature, ensure that your firewall is configured to permit the IP address to pass through the Sterling External Authentication Server.
We will now verify the available rate limit for the customer associated with the given IP address.
As developers, we will save this information in our database. Each time a request is received, we will assess the rate limit for that partner.
If the request falls within the allowed rate limit, it will be forwarded to the appropriate API service.
Additionally, we can implement another check to monitor the number of requests made by the partner within a defined time frame. For instance, we could allocate a limit of 1,000 requests per hour for a specific partner based on their IP address.
To put this into action, we will track the number of requests made by the partner.
If any conditions fail, we will provide the relevant error code and description to the partner. They will need to rectify the issue by upgrading their subscription with the service provider.
When we integrate this functionality into Sterling Integrator, we can incorporate rate limiting within a generic process. If the result is positive, the request will then be directed to the appropriate API service business process.
I recommend implementing API capabilities in Sterling Integrator rather than using specific API tools for small and medium business who is already using Sterling Integrator for their EDI integrations .Given the business capacity, Sterling Integrator can effectively expose API services to the external world. It offers robust error handling features and a clear understanding of error codes, making it particularly suitable for small and medium-sized businesses.
The Sterling Integrator Server offers enhanced functionality, equipped with a wider array of services and adapters, allowing us to implement simple functions without the need for coding.
Tracking requests and generating reports is a breeze with the Sterling File Gateway.
While this tool primarily focuses on managing EDI-based transactions, it can also be effectively utilized for API service implementations.
There is a wealth of Sterling technical resources available in the market.
One important consideration when using Sterling Integrator as an API endpoint is that it only supports XML-based transactions and requests, excluding JSON format. To address this limitation, we can create an alternative solution by leveraging the Java Task Service to develop a Java program that formats JSON.
1. One minor limitation of the API toolscurrently on the market is that implementing any functionality requires coding in a language chosen by the organization or developer.
Maintaining this code can also pose challenges within the organization.
Should there be any updates or changes to the service in the future, it may necessitate hiring new personnel with expertise in the original programming language or rewriting the functionality in a different language altogether.
Additionally, as a centralized access point, an API serves as a gateway that can attract the attention of hackers. If an API is breached, it can expose all connected applications and systems to potential threats.
Friday, August 30, 2024
Detailed process of AI System Claims Management
AI-powered claims management systems are transforming the insurance and healthcare industries by automating and optimizing the claims process. Here’s a detailed breakdown of the process involved in AI system claims management:
### 1. **Data Collection and Ingestion**
- **Initial Data Capture**: The system collects all relevant data related to a claim. This includes information from various sources such as claim forms, medical records, invoices, images, and supporting documents.
- **Data Integration**: The system integrates data from different channels, such as emails, electronic health records (EHR), insurance databases, and customer portals. AI can also extract data from unstructured formats like PDFs or images using Optical Character Recognition (OCR).
### 2. **Claim Intake and Triage**
- **Automated Triage**: The AI system classifies and categorizes claims based on severity, complexity, and urgency. It assigns claims to the appropriate workflow or team for further processing.
- **Prioritization**: High-priority claims, such as those involving critical medical conditions or significant financial loss, are flagged for immediate attention.
- **Fraud Detection**: AI models analyze claims for patterns indicative of fraud. This includes checking for inconsistencies in the data, unusual billing patterns, or mismatches with historical data.
### 3. **Data Validation and Verification**
- **Cross-Verification**: The system cross-verifies the claim data against internal databases (e.g., policy details, prior claims history) and external sources (e.g., medical databases, third-party services) to ensure accuracy.
- **Automated Validation**: AI algorithms validate claim details, such as ensuring that the treatment or service claimed is covered under the policy, and that the claim amount is within permissible limits.
- **Anomaly Detection**: The system identifies and flags any anomalies or inconsistencies in the claim data that may require manual review.
### 4. **Claims Processing and Decision Making**
- **Automated Decision Engines**: The AI system uses predefined business rules, machine learning models, and historical data to make decisions on claim approvals, denials, or adjustments.
- **Policy Adherence**: The system ensures that decisions are aligned with policy terms, conditions, and coverage limits.
- **Natural Language Processing (NLP)**: For text-based claims (e.g., medical reports or customer statements), NLP algorithms extract relevant information and insights to aid in decision-making.
### 5. **Claim Adjudication**
- **Automated Adjudication**: Claims that meet all criteria are automatically adjudicated, resulting in faster processing times and reduced manual intervention.
- **Escalation for Review**: Complex or high-value claims, as well as those flagged by the system for potential issues, are escalated for manual review by claims adjusters.
- **Feedback Loop**: The system continuously learns from adjudication outcomes to improve its decision-making accuracy over time.
### 6. **Communication and Customer Interaction**
- **Automated Notifications**: The system generates and sends automated notifications to claimants about the status of their claims, required documentation, and next steps.
- **Chatbots and Virtual Assistants**: AI-powered chatbots provide real-time assistance to claimants, answering questions, guiding them through the claims process, and helping resolve issues.
- **Document Requests**: If additional information is needed, the system can automatically request documents or clarification from the claimant or other involved parties.
### 7. **Payments and Settlement**
- **Payment Processing**: Once a claim is approved, the AI system initiates payment processing, ensuring that the correct amount is disbursed to the right party.
- **Audit Trail**: The system maintains a detailed audit trail of the entire claims process, including decision-making steps, communications, and transactions.
- **Automated Adjustments**: If adjustments to the claim amount are necessary, the system calculates the appropriate adjustments and processes the payment accordingly.
### 8. **Post-Processing and Reporting**
- **Analytics and Reporting**: The system generates detailed reports on claims performance, processing times, payment accuracy, and fraud detection outcomes. These reports provide insights into operational efficiency and areas for improvement.
- **Regulatory Compliance**: AI ensures that all claims are processed in accordance with regulatory requirements. The system can automatically generate the necessary documentation for audits and compliance reviews.
- **Continuous Improvement**: Machine learning models are continuously updated with new data to enhance the accuracy and efficiency of the claims management process.
### 9. **Fraud Detection and Prevention**
- **Predictive Modeling**: AI systems use predictive analytics to identify potential fraud before it happens by analyzing patterns and behaviors associated with fraudulent claims.
- **Real-Time Alerts**: The system generates real-time alerts for suspicious claims, allowing investigators to take prompt action.
- **Machine Learning**: AI models are trained on vast datasets to recognize subtle signs of fraud that may not be apparent to human reviewers.
### 10. **Customer Experience Enhancement**
- **Personalization**: AI systems tailor communications and interactions based on the claimant’s profile, previous interactions, and preferences.
- **Proactive Service**: AI can proactively notify customers of potential issues or opportunities, such as identifying eligible claims that haven’t been filed yet or suggesting preventive measures to avoid future claims.
### Benefits of AI in Claims Management:
- **Efficiency**: AI significantly reduces the time required to process claims, leading to faster settlements and improved customer satisfaction.
- **Accuracy**: Automated validation and decision-making reduce errors and ensure consistent application of policy terms.
- **Cost Savings**: By automating routine tasks and detecting fraud early, AI systems help reduce operational costs and prevent financial losses.
- **Scalability**: AI systems can handle large volumes of claims simultaneously, making them ideal for large insurance companies and healthcare providers.
- **Enhanced Decision-Making**: AI augments human decision-making with data-driven insights, leading to more informed and fair outcomes.
AI-powered claims management systems enhance the efficiency, accuracy, and scalability of the claims process while providing a better experience for both customers and claims adjusters.
Sunday, August 4, 2024
JSON to XML and XML to JSON converter in second . Use it for API integrations and Web development projects
Wednesday, July 24, 2024
Saturday, January 20, 2024
What are the steps to follow to integrate VMS with Banks for vendor payment | Amazon | VendorPayments|Walmart|Integration|EDI|B2B|Security
Integrating a vendor management system (VMS) with banks for vendor payment involves several steps to ensure a seamless and secure payment process. Here's a comprehensive overview of the integration process:
Step 1: Define requirements and objectives
Clearly define the objectives of integrating the VMS with banks for vendor payment. Identify the specific payment methods, data exchange formats, and security protocols that need to be supported. This will help in selecting the appropriate integration approach and tools.
Step 2: Select a VMS and bank connectivity solution
Choose a VMS that offers integration capabilities with multiple banks and supports various payment methods. Evaluate the compatibility of the VMS with the bank's payment systems and ensure it meets your specific requirements.
Step 3: Establish data exchange standards
Determine the data exchange standards that will be used for transmitting payment information between the VMS and the bank. Common standards include XML, EDI, and SWIFT. Ensure that both systems can communicate effectively using the chosen standards.
Step 4: Implement data mapping and transformation
Map the data fields in the VMS to the corresponding fields in the bank's payment systems. This may involve data transformation, such as formatting and conversion, to ensure compatibility. Develop data validation rules to ensure data integrity and prevent errors.
Step 5: Configure payment workflows
Define the payment workflows between the VMS and the bank. This includes specifying the authorization process, payment initiation, and reconciliation procedures. Establish clear roles and responsibilities for each step in the workflow.
Step 6: Conduct testing and validation
Perform thorough testing to ensure the integration is functioning as expected. Test various payment scenarios, including single payments, batch payments, and error handling. Validate data accuracy, transaction processing, and communication between the VMS and the bank.
Step 7: Deploy and monitor the integration
Deploy the integrated solution to a production environment and monitor its performance closely. Continuously review and refine the integration to address any issues or optimize the payment process.
Additional considerations for secure integration:
-
Employ strong encryption and authentication mechanisms to protect sensitive payment data.
-
Implement access controls and user authorization to restrict access to payment information based on user roles and permissions
-
Conduct regular security audits and vulnerability assessments to identify and address potential security risks.
-
Follow industry standards and best practices for secure payment processing.
Integrating a vendor management system (VMS) with banks for vendor payment involves several steps to ensure a seamless and secure payment process. Here's a comprehensive overview of the integration process:
Step 1: Define requirements and objectives
Clearly define the objectives of integrating the VMS with banks for vendor payment. Identify the specific payment methods, data exchange formats, and security protocols that need to be supported. This will help in selecting the appropriate integration approach and tools.
Step 2: Select a VMS and bank connectivity solution
Choose a VMS that offers integration capabilities with multiple banks and supports various payment methods. Evaluate the compatibility of the VMS with the bank's payment systems and ensure it meets your specific requirements.
Step 3: Establish data exchange standards
Determine the data exchange standards that will be used for transmitting payment information between the VMS and the bank. Common standards include XML, EDI, and SWIFT. Ensure that both systems can communicate effectively using the chosen standards.
Step 4: Implement data mapping and transformation
Map the data fields in the VMS to the corresponding fields in the bank's payment systems. This may involve data transformation, such as formatting and conversion, to ensure compatibility. Develop data validation rules to ensure data integrity and prevent errors.
Step 5: Configure payment workflows
Define the payment workflows between the VMS and the bank. This includes specifying the authorization process, payment initiation, and reconciliation procedures. Establish clear roles and responsibilities for each step in the workflow.
Step 6: Conduct testing and validation
Perform thorough testing to ensure the integration is functioning as expected. Test various payment scenarios, including single payments, batch payments, and error handling. Validate data accuracy, transaction processing, and communication between the VMS and the bank.
Step 7: Deploy and monitor the integration
Deploy the integrated solution to a production environment and monitor its performance closely. Continuously review and refine the integration to address any issues or optimize the payment process.
Additional considerations for secure integration:
-
Employ strong encryption and authentication mechanisms to protect sensitive payment data.
-
Implement access controls and user authorization to restrict access to payment information based on user roles and permissions
-
Conduct regular security audits and vulnerability assessments to identify and address potential security risks.
-
Follow industry standards and best practices for secure payment processing.
Thursday, August 4, 2022
How do we resolved first time FTPS connectivity issue with partner using IBM B2B Sterling Integrator
😟😟😟Background of Actual problem :
I am working for Banking client who is doing business with their partners by sending payment files using different communication channels like SFTP , HTTP , API etc. For first time one partner come up with integration requirement by using FTPS communication which is new to our banking client. My client using IBM Sterling Integrator as B2B/EDI tool to do integration with partners and this is the first partner using FTPS connectivity. While implementing and getting connectivity established with partner , we encountered many issues with their FTPs Server.
😮😮😮Problem Statement :
When we trying to connect and to do list out the files which are available in their remote directory , initially we are getting handshake failure and cannot move forward to do list files operation. We have already opened outbound ports at bank firewall and customer are also opened bank ports at their side. As part of analysis we have asked partner to provide acceptable ciphers at their side and compare with ciphers which are configured at Bank side.while initial analysis we found that there is Ciphers mismatch at handshake and it causes the issue.
😲😲😲Suggestion :
To resolve this issue, we have conducted multiple debugging sessions with all the stakeholders partner , Bank's team (myself) , Network team , operating system admin and B2B application vendor etc. In each session we have implemented below suggestions/changes mentioned at B2B server level by B2B vendor team and did the testing in meeting when all the stake holders are present and do the monitoring the traffic.Initially we asked to do below mentioned changes at their FTPS server side and they didn't aggree to do changes. Partner side they cannot make necessary changes to accepts ciphers which are configured at bank because already they are integrated with their partners and they dont want to expect any issues with their partners by cipher changes.
- SNI need to be disabled
- TLS 1.3 version need to disabled if it is enabled already and TLS1.2 version should be default
<script async src="https://pagead2.googlesyndication.com/pagead/js/adsbygoogle.js?client=ca-pub-3718162507869387"
crossorigin="anonymous"></script><script async src="https://pagead2.googlesyndication.com/pagead/js/adsbygoogle.js?client=ca-pub-3718162507869387"
crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<!-- MySquareAd -->
<ins class="adsbygoogle"
style="display:block"
data-ad-client="ca-pub-3718162507869387"
data-ad-slot="5896879220"
data-ad-format="auto"
data-full-width-responsive="true"></ins>
<script>
(adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push({});
</script>
Comparison of the latest IBM Sterling Integrator map editor vs. IBM Transformation Extender (ITX) map editors
Here’s a comparison of the latest IBM Sterling Integrator map editor vs. IBM Transformation Extender (ITX) map editor from a data-mapping p...
-
Inbound Flow: 1) The inbound, EDI data needs to be collected. 2) The collected data should be De-enveloped (removing the headers) to get t...
-
Sterling Integrator Administaration Related Interview Questions : ...
-
Encoding Conversion (From ISO8859_1 / ISO-8859_1 / ISO_8859_1 to UTF8 and vice versa) There is one service called “Encoding Conversion” in...