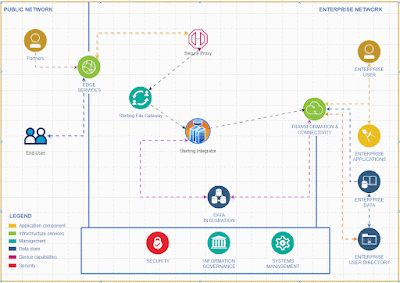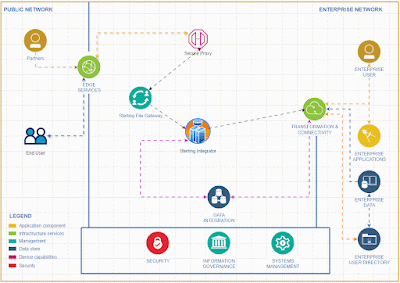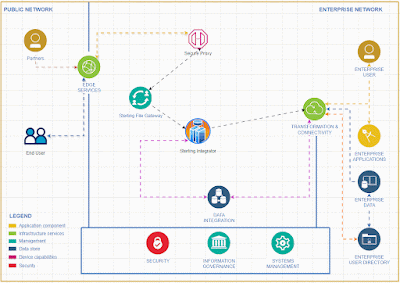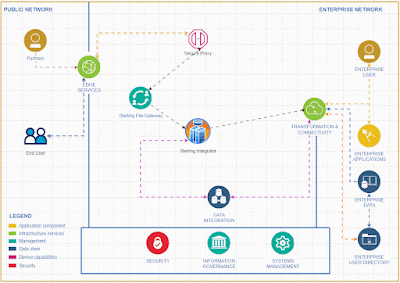
In the rapidly evolving landscape of financial technology, open banking stands
out as a transformative movement, redefining how data is shared and utilized
across the financial ecosystem. By leveraging APIs (Application Programming
Interfaces) to securely share financial information between institutions and
third-party providers, open banking has paved the way for a new era of
competition and innovation. This paradigm shift not only fosters a more dynamic
and inclusive financial market but also highlights the critical importance of
security in managing and protecting sensitive financial data. The article delves
into an overview of open banking, elaborating on its advantages such as enhanced
competition, increased innovation, and improved customer experiences.
Open Banking Overview
Open banking, also referred to as "open bank data," is a practice that
revolutionizes the traditional banking system by providing third-party financial
service providers with open access to consumer banking, transaction, and other
financial data from banks and non-bank financial institutions through
application programming interfaces (APIs). This system enables the networking of
accounts and data across institutions, which can be utilized by consumers,
financial institutions, and third-party service providers. The core of open
banking lies in its ability to allow access and control of consumer banking and
financial accounts through third-party applications. This access is typically
granted by the consumers themselves, who must provide consent, such as agreeing
to terms of service on an application. The APIs used in open banking facilitate
a variety of services, including comparing financial products, aggregating data
for marketing purposes, or conducting transactions on behalf of the consumer.
One of the pivotal benefits of open banking is its potential to reshape the
competitive landscape of the banking industry. By promoting a network-based
rather than a centralized system, open banking enhances the ability of financial
services customers to securely share their financial data with other
institutions. For instance, open banking APIs can simplify the process of
switching bank services or identifying the most suitable financial products for
consumers, thereby fostering both innovation and competition. However, open
banking also introduces significant challenges, particularly in terms of
security and privacy. The wide sharing of consumer data increases the risks of
data breaches and financial fraud. It is crucial for open banking frameworks to
implement robust security measures to protect consumer information and ensure
the integrity of financial transactions. Globally, the implementation of open
banking varies. Regions like the UK and European Economic Area have adopted a
regulatory approach, mandating banks to develop open banking frameworks. In
contrast, countries like the US, Singapore, and India have taken a market-led
approach, which may lead to faster innovation but also inconsistencies in
standards and practices. In conclusion, open banking represents a transformative
development in the financial services sector, offering significant benefits in
terms of innovation and consumer choice, but also requiring careful management
of the associated risks.
Advantages of Open Banking
Convenience and Efficiency Open banking significantly enhances the convenience
and efficiency of financial management. By allowing the aggregation of account
information into a single dashboard, open banking enables customers to view all
their financial data in one place, simplifying the way they interact with their
finances. Additionally, open banking can expedite the approval processes for
financial products such as mortgages, reducing the need for extensive paperwork
and saving valuable time. This streamlined approach not only improves the user
experience but also accelerates decision-making and financial transactions,
benefiting both consumers and businesses.
Personalization of Services
The personalization of financial services is a key advantage of open banking.
Through the use of APIs, financial service providers can access a wealth of
customer data, enabling them to offer tailored financial products and advice.
This can include everything from personalized budgeting tools and investment
advice to custom loan offers that match the user's financial profile. For
businesses, open banking facilitates the delivery of specialized financial
services such as targeted lending solutions or treasury services, enhancing
customer satisfaction and engagement.
Security and Trust
Open banking also offers improved security and builds trust among users. By
implementing strong customer authentication protocols and ensuring that
financial transactions go through rigorous security checks, open banking reduces
the risk of fraud and unauthorized access. Customers have granular control over
their data, deciding who can access their information and to what extent, which
enhances their confidence in using open banking platforms. Moreover, the use of
blockchain technology in open banking provides an additional layer of security,
making data exchanges virtually tamper-proof. This robust security framework not
only protects consumers but also fosters trust in the open banking ecosystem,
encouraging more users to embrace these innovative financial services.
Challenges and Risks Regulation and Compliance
Navigating the complex landscape of regulatory requirements presents a
significant challenge in open banking. Financial institutions and third-party
providers must adhere to diverse data protection, consumer rights, and
anti-money laundering regulations that vary across jurisdictions . This
complexity can hinder the consistency and speed of open banking adoption, as
entities must ensure compliance with evolving standards to avoid legal
repercussions.
Security Concerns
The sharing of sensitive financial data inherent in open banking increases the
risk of unauthorized access, data breaches, and misuse of personal information.
To mitigate these risks, robust security measures including encryption,
authentication, and intrusion detection systems are essential. Additionally, the
integration of third-party services exacerbates security concerns, as these
entities often become new targets for cyber-attacks, potentially increasing the
vulnerability of the entire banking ecosystem.
Consumer Trust
Building and maintaining consumer trust is crucial for the success of open
banking. Transparent communication and explicit consent for data sharing are
fundamental to assuring customers of their data's security. However, challenges
arise as consumers may not fully understand or trust the open banking framework,
especially in regions where it is a relatively new concept. Educating consumers
about the benefits and risks of open banking is vital to fostering acceptance
and promoting its safe use. Future of Open Banking The future of open banking is
poised for substantial growth and transformation, driven by technological
advancements and increasing global adoption. The open banking market is expected
to expand significantly, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of
46.94%, reaching an estimated value of USD 552,620.35 million by 2028 .
Emerging Trends
Several emerging trends are shaping the future of open banking. The integration
of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning
(ML), and big data analytics is anticipated to enhance the functionality and
scope of open banking services. These technologies enable the personalization of
financial services, offering consumers tailored financial advice, automated
savings plans, and customized investment recommendations. Additionally, the
expansion of the open banking ecosystem and the focus on customer-centric
solutions are expected to drive innovation and improve the user experience.
Blockchain technology is also emerging as a key player in the open banking
landscape, providing enhanced security and transparency for financial
transactions . The adoption of standardized APIs across the industry is
improving interoperability between financial institutions and fintech firms,
further facilitating the seamless exchange of financial data.
Potential Market Growth
The open banking market is experiencing robust growth across various regions. In
Europe, the adoption of open banking solutions is accelerating, positioning the
region at the forefront of the open banking movement. This growth is supported
by the increasing investment in advanced technologies and a strong regulatory
framework that promotes innovation and competition. In North America, the market
is driven by consumer demand for digital financial services, encouraging banks
to invest in open banking APIs and collaborate with fintech firms . The Asia
Pacific region is witnessing the fastest growth, driven by a surge in digital
payment services and a growing awareness of the benefits of open banking . The
Middle East and Africa are also seeing significant growth, with regulatory
frameworks supporting the adoption of open banking. The future of open banking
represents a paradigm shift in the financial services industry, offering
promising opportunities for innovation, enhanced security, and improved customer
experiences. As the sector continues to evolve, it will likely play a crucial
role in shaping the landscape of global financial services.
Conclusion
Throughout this exploration of open banking, we've delved into its significant
capacity to revolutionize the financial landscape by enabling enhanced data
sharing and fostering innovation. We've recounted the essential benefits that
open banking presents, such as personalized financial services, increased
efficiency, and heightened security, alongside acknowledging the hurdles it
faces, including regulatory compliance, security concerns, and the vital need
for consumer trust. By examining these facets, the article has underscored open
banking's pivotal role in driving technological advancements within the fintech
industry, showcasing its potential to radically transform consumer experiences
and the competitive dynamics among financial providers. As we gaze into the
future, the trajectory of open banking appears inherently linked with the
continuous evolution of technology and regulatory frameworks, suggesting a
landscape ripe with opportunities for both consumers and businesses. The
anticipated expansion and integration of emerging technologies, like AI and
blockchain, with open banking platforms, promise to further refine and secure
the financial services ecosystem, paving the way for a more interconnected and
efficient market. Thus, the journey of open banking, while replete with
challenges, stands as a beacon of innovation, with its unfolding story poised to
redefine the essence of financial services in an increasingly digital world.
FAQs
1. How is fintech reshaping the banking industry? Fintech companies are
revolutionizing the banking sector by significantly improving customer
experiences. These companies are known for their speed, affordability,
efficiency, and enhanced security compared to traditional banking institutions.
2. What does the future hold for Open Banking? The future of Open Banking looks
very promising, with expectations for its growth and adoption to continue
rising. According to a Forrester report, the number of Open Banking users in
Europe is projected to double by the year 2027. 3. What are the advantages of
using Open Banking? Open Banking offers numerous benefits, including: Access to
a broader array of financial services. Improved personalization and customer
experience in banking. Greater control and enhanced security over one's
financial data. Promotion of innovation and competition within the banking
sector. Better account management. Enhanced budget management and financial
analysis capabilities. Easier and simplified payment and transfer processes. 4.
In what ways will fintech services improve the banking experience? Fintech
companies utilize data analytics and artificial intelligence to provide
personalized financial services. These tailored services meet individual needs
and preferences, significantly enhancing the overall customer experience in
banking.
References
[1] - https://www.investopedia.com/terms/o/open-banking.asp
[2] -
https://paymentsconsulting.com/open-banking-five-principles-for-success/
[3] - https://www.mastercard.com/news/perspectives/2022/open-banking-101/
[4] -
https://humansofglobe.com/unlocks-the-future-of-personalized-finance-with-open-banking/
[5] - https://www.sydle.com/blog/open-banking-65030cf8697d3e430a055739
[6] - https://stripe.com/resources/more/open-banking-explained
[7] -
https://gocardless.com/guides/posts/what-are-the-benefits-of-open-banking/
[8] -
https://www.ey.com/en_ca/banking-capital-markets/building-customer-trust-in-open-banking-through-security-transformation
[9] -
https://www.financemagnates.com/fintech/payments/overcoming-security-and-privacy-concerns-in-open-banking/
[10] - https://www.getfocal.ai/knowledgebase/what-is-open-banking
[11] - https://seon.io/resources/open-banking-risk-and-fraud/
[12] -
https://www.openbankproject.com/blog/open-banking-10-challenges-for-regulators/
[13] -
https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/open-banking-market-future-growth-developments-6edqf/
[14] -
https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/Market-Reports/open-banking-solutions-market-160940134.html
[15] -
https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/open-banking-systems-market
[16] -
https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/ResearchInsight/emerging-trends-in-open-banking-solutions-market.asp
[17] -
https://www.powens.com/blog/9-open-banking-trends-predicted-to-dominate-in-2023/

.png)