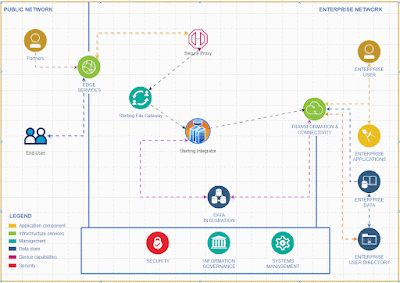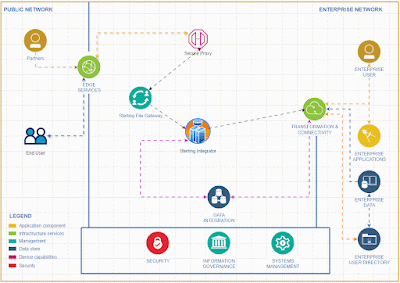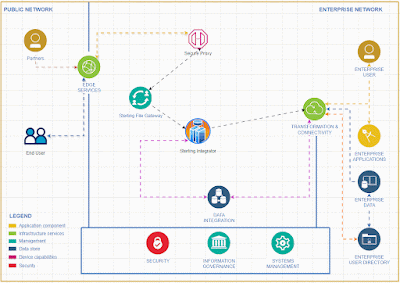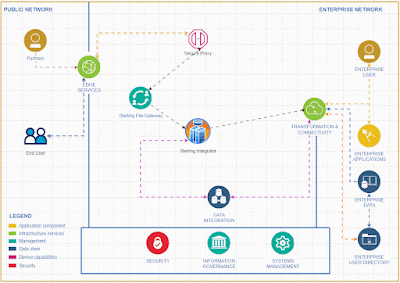
Here’s a comparison of the latest IBM Sterling Integrator map editor vs. IBM Transformation Extender (ITX) map editor from a data-mapping perspective, focusing on capabilities, user experience, advanced features, and typical use-cases. Both tools are part of the IBM B2B/Integration ecosystem but serve slightly different purposes. (ibm.com)
📌 1) Overview: Purpose & Positioning
IBM Sterling Integrator Map Editor
-
Primary map tool bundled with IBM Sterling B2B Integrator, used for EDI and file transformation maps within Sterling workflows.
-
Runs as a Windows standalone client and is mainly used to create/check-in maps that are executed by the Sterling translation engine.
-
Supports formats such as EDI (X12/EDIFACT), positional, flat, XML, SQL and native support for Sterling standard rule types.
-
Typical use-case: transaction partner onboarding, simple to moderately complex data translation within B2B Integrator business processes.
-
Focused on Sterling environments and its own translation engine (integrated with B2B Integrator). (ibm.com)
IBM Transformation Extender (ITX) Map Editor
-
A universal transformation engine and graphical map editor that can be used independently or with Sterling Integrator.
-
Designed for complex, high-volume any-to-any transformation (including XML, JSON, industry standards, and custom formats).
-
Can be invoked by Sterling B2B Integrator via services (like the WTX/ITX map service), or run standalone in other integration scenarios.
-
Suitable where extensive industry pack support and advanced transformation features are required (e.g., advanced validations, nested loops, cross lookups). (ibm.com)
🧭 2) Mapping Capabilities
Sterling Integrator Map Editor
-
Single input → single output maps (typical EDI or file to file) with conditionals & simple loops.
-
Uses standard rules and extended rules for EDI segment logic, but has limited advanced validation relative to ITX.
-
UI is traditional and designed around Sterling data formats with specific EDI handling tools (e.g., DDF/IFD definitions).
-
Mapping control is tied into the Sterling translation engine that B2B Integrator runs at runtime.
-
Best for organizations focused primarily on EDI and typical EDI to XML or flat file conversion tasks. (public.dhe.ibm.com)
ITX Map Editor
-
Any-to-any transformations: multiple source schemas to multiple target schemas.
-
Includes industry packs for healthcare, supply chain, finance and supports advanced formats with rich validation.
-
Provides flexible rule sets, looping constructs, lookups, and advanced data logic.
-
Designed for complex transformation logic, often beyond what Sterling Map Editor supports natively (e.g., multi-input multi-output, advanced lookups).
-
ITX maps can also be run within Sterling but may need the ITX/ITXA integration setup. (ibm.com)
🧠 3) User Experience & Productivity
Sterling Integrator Map Editor
✔ Classic client with drag-and-drop for Sterling formats
✔ Works directly with Sterling map repository (check-in/checkout)
✔ Easier for users focused on B2B EDI use-cases
⚠ Limited modern UX improvements compared to ITX
⚠ Simpler logic constructs relative to Transformation Extender
ITX Map Editor
✔ Highly flexible map design UI
✔ Better suited for power users needing advanced transformations
✔ Often perceived as more scalable & versatile for enterprise-wide data projects
⚠ Requires understanding of transformation engine concepts
⚠ Integration with Sterling may require additional configuration
🏗️ 4) Execution & Platform Integration
Sterling Map Editor
-
Maps run via Sterling translation service inside Sterling Integrator processes.
-
Doesn’t natively require the ITX engine unless calling external transforms.
-
Best optimized for Sterling business process maps. (ibm.com)
ITX Map Editor
-
Maps can run standalone or inside Sterling via the WTX Map/ITX map service.
-
ITX is more modular and supports REST APIs, containerized runtimes, and cloud deployment capabilities (recent versions).
-
More suitable for hybrid, multi-platform integration landscapes beyond traditional EDI. (ibm.com)
📊 5) Key Differences (Quick Summary)
| Feature / Capability | Sterling Integrator Map Editor | ITX Map Editor |
|---|---|---|
| Target audience | B2B Integrator users | Integration & transformation specialists |
| Transformation complexity | Moderate | High |
| Supported map patterns | Mostly single input/output | Multi input/output, nested logic |
| Industry pack support | Basic | Extensive (healthcare, finance, etc.) |
| Integration with Sterling | Native | Via services |
| Deployment options | Windows-based | Standalone, cloud/container |
📌 When to Prefer Each
✅ Use Sterling Map Editor when:
-
Your primary goal is EDI or simple file/flat-to-XML transformations in a Sterling business workflow.
-
You want deep integration with B2B Integrator repository & check-in/out processes.
✅ Use ITX Map Editor when:
-
You need complex, highly flexible data transformations, cross-industry processing, or any-to-any logic.
-
You want a tool usable outside Sterling (e.g., in microservices, API-based architectures).
-
You plan to reuse transformation logic across multiple platforms. (ibm.com)
📌 Final Takeaway
Both editors serve mapping purposes within the IBM ecosystem, but:
-
Sterling Integrator’s map editor is optimized for B2B/EDI transformations in Sterling workflows with straightforward capabilities.
-
ITX (Transformation Extender) offers a richer, more universal transformation engine suited for complex integration needs that extend beyond typical B2B use-cases.
If you are upgrading or architecting future solutions, consider using ITX for complex transformations and Sterling Map Editor for core B2B integration tasks. (ibm.com)


.png)