Thursday, May 1, 2025
Automate Resume Screening with TAOne.AI | Fast & Smart Talent Filtering Process 500+ Resumes in Hour
Thursday, January 2, 2025
Implementing EDI Integration Using Microsoft Azure Logic Apps
# Implementing EDI Integration Using Microsoft Azure Logic Apps
This comprehensive guide provides a step-by-step approach to implementing EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) integration using Microsoft Azure Logic Apps. Azure Logic Apps is a cloud-based service designed to help automate workflows and integrate EDI transactions seamlessly with your systems and trading partners.
---
## **Step 1: Prerequisites** Before starting the implementation, ensure you have the following:
1. **Azure Subscription**: - Sign up for an Azure account if you don’t already have one. - Access the Azure Portal.
2. **Trading Partner EDI Specifications**: - Obtain the EDI implementation guide for the documents you will exchange (e.g., EDI 810, EDI 850).
3. **Existing Systems**: - Identify the systems (e.g., ERP, CRM) that will integrate with EDI workflows.
4. **Data Format**: - Define the data format (e.g., X12, EDIFACT, XML) based on trading partner requirements.
---
## **Step 2: Create a Logic App** 1. **Log in to Azure Portal**: - Navigate to the Azure portal and search for "Logic Apps."
2. **Create a New Logic App**: - Click "Create" and provide the following details: - **Resource Group**: Create or select an existing resource group. - **Name**: Name your Logic App (e.g., `EDI_Integration_Workflow`). - **Region**: Select the appropriate region for hosting.
3. **Open Logic App Designer**: - Open the Logic App in Designer mode to start building your workflow.
---
## **Step 3: Add EDI Integration Connector** Azure provides built-in connectors for EDI transactions, such as AS2, X12, and EDIFACT.
### **For X12 EDI** 1. **Set Up an Integration Account**: - Navigate to "Integration Accounts" in the Azure portal. - Create an Integration Account and link it to your Logic App.
2. **Upload Partner Agreements**: - Define trading partners and upload their details (e.g., X12 schemas, certificates, and agreements) into the Integration Account. - Add: - **Schemas**: Import X12 schema files for the EDI document types you are processing. - **Partners**: Add trading partner details (identifiers, roles, and agreements). - **Agreements**: Configure inbound and outbound agreements specifying EDI protocols and settings.
3. **Configure X12 Connector**: - In the Logic App Designer, search for "EDI X12" and add the X12 connector. - Choose "Receive X12 Message" or "Send X12 Message" based on the workflow.
---
## **Step 4: Design the Workflow**
### **Inbound EDI Workflow** 1. **Receive EDI Document**: - Add a trigger to start the Logic App, such as "When a file is added to Azure Blob Storage" or "Receive AS2 message."
2. **Decode EDI Message**: - Use the "EDI Decode" action to validate and parse the received EDI document. - Map the EDI segments to readable data (e.g., JSON, XML).
3. **Transform Data**: - Add a "Transform XML" action to convert the EDI message into the desired format for your system. - Use a predefined map or create one using Azure’s mapping tools.
4. **Send Data to System**: - Add an action to send the transformed data to your internal system (e.g., SQL Database, Dynamics 365).
### **Outbound EDI Workflow** 1. **Receive Data from System**: - Add a trigger to listen for new data in your system (e.g., "When an item is created in SQL Database").
2. **Transform Data**: - Use the "Transform XML" action to convert internal data into the required EDI format.
3. **Encode EDI Message**: - Use the "EDI Encode" action to package the data into an X12-compliant EDI document.
4. **Send EDI Document**: - Add an action to send the EDI document to the trading partner via AS2, FTP, or another protocol.
---
## **Step 5: Test the Integration** 1. **Enable Logging**: - Use Azure Monitor or Application Insights to track the execution of your Logic App.
2. **Perform Test Runs**: - Simulate inbound and outbound transactions using test data. - Verify that the EDI documents are generated, validated, and transmitted correctly.
3. **Fix Errors**: - Debug any errors using the Logic App’s run history and logs.
---
## **Step 6: Go Live** 1. **Deploy the Logic App**: - Ensure all configurations are in place and move the Logic App to production.
2. **Monitor Live Transactions**: - Use Azure’s monitoring tools to ensure smooth operation and address any issues promptly.
---
## **Step 7: Maintain and Optimize** 1. **Periodic Reviews**: - Review workflows to ensure compliance with updated trading partner requirements.
2. **Optimize Performance**: - Monitor latency and throughput, and adjust Logic App triggers and actions as needed.
3. **Add New Partners**: - Scale your solution by adding new trading partners or EDI document types.
---
By following this detailed roadmap for implementing EDI integration using Azure Logic Apps, you can streamline your business processes, ensure compliance with trading partner requirements, and achieve efficient and reliable electronic data exchange.
Friday, December 27, 2024
Implementing the EDI 810 (Invoice) document in SPS Commerce
Implementing the EDI 810 (Invoice) document in SPS Commerce involves configuring the tool to map, transmit, and validate the EDI data according to trading partner requirements. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
---
### **Step 1: Gather Requirements**
1. **Understand Trading Partner Specifications**: Obtain the 810 EDI Implementation Guide (specifications) from your trading partner.
- Identify required segments, elements, and codes.
- Understand any validation rules or business-specific requirements.
2. **Define Business Rules**: Work with internal teams to outline the invoicing data flow and confirm all necessary data points are captured.
---
### **Step 2: Configure SPS Commerce Tool**
1. **Log in to SPS Commerce Fulfillment**:
- Access the web portal or integration tool provided by SPS Commerce.
- Ensure you have administrative privileges to configure document settings.
2. **Set Up Trading Partner Connection**:
- Navigate to the "Connections" or "Trading Partner Setup" section.
- Add or update the trading partner's profile to enable the 810 document type.
3. **Enable EDI 810 Document**:
- Locate the document setup menu for the trading partner.
- Select "810 Invoice" and ensure it is enabled.
4. **Map Data Fields**:
- Use SPS Commerce’s mapping tools to map your internal data (ERP or accounting system) to the 810 format.
- Map mandatory segments like **ST (Transaction Set Header)**, **BIG (Beginning Segment for Invoice)**, **N1 (Name)**, **IT1 (Invoice Line Items)**, and **TDS (Total Monetary Value Summary)**.
5. **Validate Mapping**:
- Perform test mapping for various scenarios (e.g., single item, multiple items, taxes, discounts).
- Ensure all required segments are mapped and optional ones are handled based on trading partner preferences.
---
### **Step 3: Test the Implementation**
1. **Generate a Test Invoice**:
- Create a sample invoice in your internal system.
- Export it to SPS Commerce.
2. **Run Mapping Validation**:
- Verify the data is translated into the correct EDI 810 format.
- Check the structure, syntax, and compliance with the trading partner’s specifications.
3. **Send Test EDI File**:
- Use the testing environment provided by SPS Commerce to transmit the 810 document to your trading partner. - Work with the trading partner to validate and troubleshoot any issues.
---
### **Step 4: Go Live**
1. **Confirm Trading Partner Approval**:
- After successful testing, obtain trading partner approval to go live.
2. **Enable Production Mode**:
- Switch the EDI 810 configuration from the test environment to production.
3. **Monitor Initial Transactions**:
- Closely monitor the first few live transactions for errors or discrepancies.
- Use SPS Commerce’s monitoring tools for error alerts and transaction tracking.
---
### **Step 5: Maintain and Update**
1. **Periodic Reviews**:
- Regularly review and update mappings to accommodate any trading partner updates or internal system changes.
2. **Error Resolution**:
- Use SPS Commerce’s error handling tools to address failed transactions.
- Work with support if needed.
3. **Expand Functionality**:
- As needed, implement additional documents (e.g., 850, 856) to enhance integration with your trading partner.
---
### Tools & Resources
- **SPS Commerce Documentation**: Reference guides and tutorials.
- **EDI Validator**: To check compliance.
- **Support Team**: Contact SPS Commerce for assistance during setup or troubleshooting.
Would you like detailed examples of specific 810 segments or mapping logic?
Sunday, November 17, 2024
Generate your trusted CRT , PEM and P12 security certificates for signing and encryption functionality for HTTP or HTTPS Communication
Monday, October 14, 2024
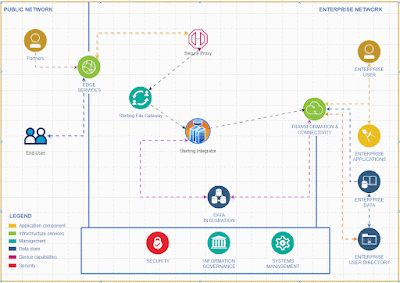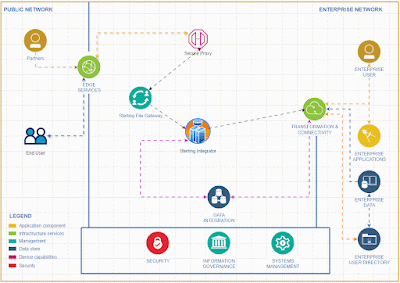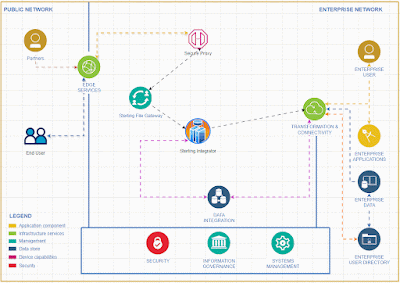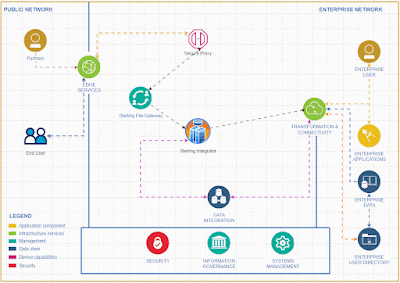
Introducing a rate limiter feature in IBM Sterling Integrator allows for comprehensive API functionality without the need to invest in additional API tools.
To activate and integrate the rate limiter feature in Sterling Integrator for comprehensive API functionality, follow these steps.To effectively deliver a service, it's essential to create a system that accepts input from clients and returns the appropriate output based on that input.
When we offer this service, it's important to pinpoint the client's IP address for any requests originating from outside our network.
To achieve the capability of identifying the client IP address within Sterling Integrator, we should adhere to the following steps.
To activate the Client IP feature, follow these steps: First, include the property client_ip_correlation_enabled=false in the jdbc.properties_platform_ifcbase_ext.in file.
Next, execute ./setupfiles.sh.
This feature captures the IP address of the client that initiates the request.
Certain clients require this functionality to comply with regulatory standards.
Before you enable the Client IP feature, ensure that your firewall is configured to permit the IP address to pass through the Sterling External Authentication Server.
We will now verify the available rate limit for the customer associated with the given IP address.
As developers, we will save this information in our database. Each time a request is received, we will assess the rate limit for that partner.
If the request falls within the allowed rate limit, it will be forwarded to the appropriate API service.
Additionally, we can implement another check to monitor the number of requests made by the partner within a defined time frame. For instance, we could allocate a limit of 1,000 requests per hour for a specific partner based on their IP address.
To put this into action, we will track the number of requests made by the partner.
If any conditions fail, we will provide the relevant error code and description to the partner. They will need to rectify the issue by upgrading their subscription with the service provider.
When we integrate this functionality into Sterling Integrator, we can incorporate rate limiting within a generic process. If the result is positive, the request will then be directed to the appropriate API service business process.
I recommend implementing API capabilities in Sterling Integrator rather than using specific API tools for small and medium business who is already using Sterling Integrator for their EDI integrations .Given the business capacity, Sterling Integrator can effectively expose API services to the external world. It offers robust error handling features and a clear understanding of error codes, making it particularly suitable for small and medium-sized businesses.
The Sterling Integrator Server offers enhanced functionality, equipped with a wider array of services and adapters, allowing us to implement simple functions without the need for coding.
Tracking requests and generating reports is a breeze with the Sterling File Gateway.
While this tool primarily focuses on managing EDI-based transactions, it can also be effectively utilized for API service implementations.
There is a wealth of Sterling technical resources available in the market.
One important consideration when using Sterling Integrator as an API endpoint is that it only supports XML-based transactions and requests, excluding JSON format. To address this limitation, we can create an alternative solution by leveraging the Java Task Service to develop a Java program that formats JSON.
1. One minor limitation of the API toolscurrently on the market is that implementing any functionality requires coding in a language chosen by the organization or developer.
Maintaining this code can also pose challenges within the organization.
Should there be any updates or changes to the service in the future, it may necessitate hiring new personnel with expertise in the original programming language or rewriting the functionality in a different language altogether.
Additionally, as a centralized access point, an API serves as a gateway that can attract the attention of hackers. If an API is breached, it can expose all connected applications and systems to potential threats.
Monday, September 30, 2024
Workato Automation Tool and main capabilities when compare to other iPAAS tools like Dell Boomi
Dears
Good Day
Hope you are doing good.
I would like to share my recent achievement: yesterday, I successfully completed the Workato Automation Pro I tool certification as part of my efforts to enhance my skill set.
Some brief introduction about Workato Automation Tool ,
Workato is an automation tool that helps businesses connect different apps and systems without needing a lot of coding. It allows you to create workflows, called "recipes," that automate tasks like sending data from one app to another or triggering actions based on events. For example, it can automatically update a spreadsheet when a new order is placed or send an email when a project status changes. Workato works with many popular apps like Salesforce, Slack, and QuickBooks, making it easier to streamline work processes and save time on repetitive tasks.
This tool boasts enhanced security features compared to another iPaaS solution, Boomi. Additionally, it offers a unique capability to retain the failed steps of a process during unexpected system failures, automatically resuming process executions once the system restarts. This means there's no need for us to manually check whether we need to reprocess any failed processes.
#integration #EDI #B2B #Workato #Salesforce #Banking #Finance #IToperations #automation #QuickBooks #insurance #Retail #API #AI #IBM #boomi #ipaas #saas
LinkedIn Post Link: [Insert your LinkedIn post link here]
Workato Automation Tool brief description about Workato automation tool in layman wordsWorkato is an automation tool that helps businesses connect different apps and systems without needing a lot of coding. It allows you to create workflows, called "recipes," that automate tasks like sending data from one app to another or triggering actions based on events. For example, it can automatically update a spreadsheet when a new order is placed or send an email when a project status changes. Workato works with many popular apps like Salesforce, Slack, and QuickBooks, making it easier to streamline work processes and save time on repetitive tasks.
Tuesday, September 3, 2024
JSON Validator , URL Encoder/Decoder , URL Parser , HTML Encoder/Decoder , HTML Prettifier/Minifier , Base64 Encoder/Decoder , JSON Prettifier/Minifier, JSON Escaper/Unescaper ,
Comprehensive Utility Tool
URL Encoder/Decoder
URL Parser
HTML Encoder/Decoder
HTML Prettifier/Minifier
Base64 Encoder/Decoder
JSON Prettifier/Minifier
JSON Escaper/Unescaper
JSON Validator
Friday, August 30, 2024
Detailed process of AI System Claims Management
AI-powered claims management systems are transforming the insurance and healthcare industries by automating and optimizing the claims process. Here’s a detailed breakdown of the process involved in AI system claims management:
### 1. **Data Collection and Ingestion**
- **Initial Data Capture**: The system collects all relevant data related to a claim. This includes information from various sources such as claim forms, medical records, invoices, images, and supporting documents.
- **Data Integration**: The system integrates data from different channels, such as emails, electronic health records (EHR), insurance databases, and customer portals. AI can also extract data from unstructured formats like PDFs or images using Optical Character Recognition (OCR).
### 2. **Claim Intake and Triage**
- **Automated Triage**: The AI system classifies and categorizes claims based on severity, complexity, and urgency. It assigns claims to the appropriate workflow or team for further processing.
- **Prioritization**: High-priority claims, such as those involving critical medical conditions or significant financial loss, are flagged for immediate attention.
- **Fraud Detection**: AI models analyze claims for patterns indicative of fraud. This includes checking for inconsistencies in the data, unusual billing patterns, or mismatches with historical data.
### 3. **Data Validation and Verification**
- **Cross-Verification**: The system cross-verifies the claim data against internal databases (e.g., policy details, prior claims history) and external sources (e.g., medical databases, third-party services) to ensure accuracy.
- **Automated Validation**: AI algorithms validate claim details, such as ensuring that the treatment or service claimed is covered under the policy, and that the claim amount is within permissible limits.
- **Anomaly Detection**: The system identifies and flags any anomalies or inconsistencies in the claim data that may require manual review.
### 4. **Claims Processing and Decision Making**
- **Automated Decision Engines**: The AI system uses predefined business rules, machine learning models, and historical data to make decisions on claim approvals, denials, or adjustments.
- **Policy Adherence**: The system ensures that decisions are aligned with policy terms, conditions, and coverage limits.
- **Natural Language Processing (NLP)**: For text-based claims (e.g., medical reports or customer statements), NLP algorithms extract relevant information and insights to aid in decision-making.
### 5. **Claim Adjudication**
- **Automated Adjudication**: Claims that meet all criteria are automatically adjudicated, resulting in faster processing times and reduced manual intervention.
- **Escalation for Review**: Complex or high-value claims, as well as those flagged by the system for potential issues, are escalated for manual review by claims adjusters.
- **Feedback Loop**: The system continuously learns from adjudication outcomes to improve its decision-making accuracy over time.
### 6. **Communication and Customer Interaction**
- **Automated Notifications**: The system generates and sends automated notifications to claimants about the status of their claims, required documentation, and next steps.
- **Chatbots and Virtual Assistants**: AI-powered chatbots provide real-time assistance to claimants, answering questions, guiding them through the claims process, and helping resolve issues.
- **Document Requests**: If additional information is needed, the system can automatically request documents or clarification from the claimant or other involved parties.
### 7. **Payments and Settlement**
- **Payment Processing**: Once a claim is approved, the AI system initiates payment processing, ensuring that the correct amount is disbursed to the right party.
- **Audit Trail**: The system maintains a detailed audit trail of the entire claims process, including decision-making steps, communications, and transactions.
- **Automated Adjustments**: If adjustments to the claim amount are necessary, the system calculates the appropriate adjustments and processes the payment accordingly.
### 8. **Post-Processing and Reporting**
- **Analytics and Reporting**: The system generates detailed reports on claims performance, processing times, payment accuracy, and fraud detection outcomes. These reports provide insights into operational efficiency and areas for improvement.
- **Regulatory Compliance**: AI ensures that all claims are processed in accordance with regulatory requirements. The system can automatically generate the necessary documentation for audits and compliance reviews.
- **Continuous Improvement**: Machine learning models are continuously updated with new data to enhance the accuracy and efficiency of the claims management process.
### 9. **Fraud Detection and Prevention**
- **Predictive Modeling**: AI systems use predictive analytics to identify potential fraud before it happens by analyzing patterns and behaviors associated with fraudulent claims.
- **Real-Time Alerts**: The system generates real-time alerts for suspicious claims, allowing investigators to take prompt action.
- **Machine Learning**: AI models are trained on vast datasets to recognize subtle signs of fraud that may not be apparent to human reviewers.
### 10. **Customer Experience Enhancement**
- **Personalization**: AI systems tailor communications and interactions based on the claimant’s profile, previous interactions, and preferences.
- **Proactive Service**: AI can proactively notify customers of potential issues or opportunities, such as identifying eligible claims that haven’t been filed yet or suggesting preventive measures to avoid future claims.
### Benefits of AI in Claims Management:
- **Efficiency**: AI significantly reduces the time required to process claims, leading to faster settlements and improved customer satisfaction.
- **Accuracy**: Automated validation and decision-making reduce errors and ensure consistent application of policy terms.
- **Cost Savings**: By automating routine tasks and detecting fraud early, AI systems help reduce operational costs and prevent financial losses.
- **Scalability**: AI systems can handle large volumes of claims simultaneously, making them ideal for large insurance companies and healthcare providers.
- **Enhanced Decision-Making**: AI augments human decision-making with data-driven insights, leading to more informed and fair outcomes.
AI-powered claims management systems enhance the efficiency, accuracy, and scalability of the claims process while providing a better experience for both customers and claims adjusters.
Sunday, August 25, 2024
To set up sales reports using SPS Commerce for EDI, you need to ensure proper configuration of your EDI processes and reports to accurately reflect sales data
### 1. **Data Integration Setup**
- **Identify Data Flow**: Determine what sales data is needed for reporting (e.g., purchase orders, invoices, inventory updates). Key documents include EDI 850 (Purchase Order), EDI 810 (Invoice), and EDI 867 (Product Transfer and Resale Report).
- **Establish Communication Channels**:
- Choose the communication method that works with your partners, such as **AS2, FTP, or VAN** (Value-Added Network).
- Ensure that your system is capable of sending and receiving EDI transactions. If you're using an ERP system like SAP, Oracle, or NetSuite, ensure it’s integrated with **SPS Commerce**.
- **Test Connectivity**: Perform end-to-end tests with trading partners to ensure EDI transactions are being sent and received properly. Use SPS Commerce’s testing tools to validate connectivity and document formats.
### 2. **Mapping Sales Data**
- **Identify Document Types**: For sales reporting, focus on key EDI document types:
- **EDI 850**: Purchase Order - Helps track orders placed by customers.
- **EDI 810**: Invoice - Details invoiced amounts and products sold.
- **EDI 856**: Advance Ship Notice - Helps track the shipments of goods.
- **EDI 867**: Product Transfer and Resale Report - Specific for reporting detailed product sales data back to the supplier.
- **EDI 846**: Inventory Inquiry/Advice - Track inventory levels for accurate sales reporting.
- **Data Mapping**: Work with your IT or EDI team to create mappings between the data in these documents and your internal business systems. Mapping ensures that each EDI field is correctly interpreted by your ERP, accounting, or CRM systems. SPS Commerce typically provides a mapping tool for this.
- **Customization**: You may need to customize mappings to reflect specific customer or supplier requirements, such as custom fields or non-standard data elements. Review your trading partner agreements for details.
### 3. **Report Configuration**
- **Define Reporting Requirements**: Define the scope of your sales reports, including the specific data points to track. For example:
- **Total Sales Volume**: Track the total amount of sales over a given period.
- **Sales by Region**: Break down sales by geographic region, if applicable.
- **Product Performance**: Track sales by product type or category.
- **Customer Segmentation**: Identify which customers are purchasing the most products.
- **Report Customization**:
- SPS Commerce’s platform includes reporting tools, often integrated with an **Analytics** module. Use these tools to create custom sales reports that pull data from multiple EDI documents.
- Choose report formats (e.g., Excel, PDF, or CSV) based on your business needs.
- Work with SPS Commerce’s support team to set up custom fields or filters that might be unique to your business.
- **Set Report Parameters**:
- Configure parameters such as time periods (e.g., daily, weekly, or monthly reports) and specific products or regions to track.
- You may also choose to set thresholds or alerts for certain key metrics (e.g., low stock levels or high sales volume).
### 4. **Scheduled and Automated Reports**
- **Set Up Recurring Reports**: Configure SPS Commerce to generate sales reports automatically on a recurring basis. You can set the frequency based on business requirements (e.g., daily, weekly, or monthly).
- **Automated Alerts**: If needed, set up automated notifications when certain thresholds are met (e.g., a sudden spike in sales or low inventory levels). These can help you take immediate action based on the data.
### 5. **Testing and Validation**
- **Run Sample Reports**: Before going live, run a few sample sales reports to ensure the data is accurate and the report format meets your needs. Check for:
- **Data Accuracy**: Ensure the report is correctly pulling sales data from EDI transactions and that no critical data is missing.
- **Report Structure**: Verify that the reports are structured correctly with proper headings, summaries, and filters.
- **Cross-check with Business Systems**: Cross-validate the EDI-generated reports with your ERP or internal systems to ensure consistency across all platforms.
- **Review with Stakeholders**: Share the reports with key stakeholders to get feedback and make any necessary adjustments to the report layout or data points.
### 6. **Live Reporting and Monitoring**
- **Go Live**: Once testing is complete and the reports meet your business requirements, implement them into your live environment.
- **Monitor Reports**: e monitor sales reports to ensure data integrity over time. Address any discrepancies immediately by working with your EDI and IT teams.
- **Adjust as Needed**: Sales reporting needs may evolve, so be prepared to adjust the report parameters or data mappings as your business grows or changes.
### 7. **Ongoing Maintenance**
- **Update Mapping and Configuration**: As trading partners update their EDI requirements or you onboard new ones, update the data mappings and report configurations.
- **New Document Types**: If new EDI documents are introduced or existing ones change (e.g., new fields in the EDI 867 for product resale reports), update your system accordingly.
- **Training**: Keep your team trained on how to interpret and utilize the sales reports generated by SPS Commerce. Also, ensure that your staff is aware of any new reporting capabilities or changes in the reporting process.
### 8. **Advanced Analytics (Optional)**
- If you need more in-depth insights beyond basic sales data, SPS Commerce offers advanced **Analytics** features:
- **Sales Trends Analysis**: Identify long-term sales trends and seasonal patterns.
- **Inventory Management**: Track inventory levels alongside sales data to ensure that stock levels are in line with demand.
- **Forecasting**: Use sales data to forecast future trends and adjust purchasing strategies accordingly.
Sunday, August 4, 2024
JSON to XML and XML to JSON converter in second . Use it for API integrations and Web development projects
Wednesday, July 24, 2024
Sunday, July 21, 2024
The Future of Invoicing: How a Unified E-Invoice Format Can Simplify Global Compliance in 2028
Most of the people knows that Germany is going to implement E-Invoicing in all sectors which aliens with global trends of digital transformation and it is spreading to all over countries in the world.
What is E-Invoicing
Invoice should be sent electronically to respective buyers in different sectors and it should
be in same standardized format which can support both sender and receiver parties.
Benefits of E-Invoicing
Cost Savings
Increased efficiency
Improved Accuracy
Increased transparancy
Easy Compliance
Faster Processing Times
Better Supplier Relationships
Here is the list of E-Invoicng formats which are using in different countries in different formats
- **PEPPOL (Pan-European Public Procurement Online)**: Used in many European countries.
- **UBL (Universal Business Language)**: Used in various countries and industries.
- **Facturae**: Spain.
- **FatturaPA**: Italy.
- **Factura XML**: Mexico.
- **e-Invoice (GST)**: India.
- **ZUGFeRD**: Germany.
In future, E-Invoice formats are different for each country and it is not easy process
invoices when doing business / buying things from different countries. Sellers will have
knowledge on the E-invoicing format which is following in their country and they feel
difficult to understand the other countries E-Invoicing formats and generate E-Invoice
in format of country from where they have received the order. Due to globalization any company
can receive orders from any where in the world and compnaies should be in position to ship the
goods / provide service and they should be in postion to create E-Invoice send to respective
customers in format which acceptable in their countries
By Analyzing multiple E-Invoicing formats which are formally allowed in different countries
and come up with common E-Invoice standard which can support any country followed / accepted E-invoice
format. So that it can work like EDI integration working between two business houses. But
it doesn't require complex EDI integration setup & maintainance and not required to buy any EDI
software applications and corresponding licenses.
To build this common invoice standard we can use some open source inhouse application which can support receive invoices or generate invoices in standard format and converted into country specific E-Invoice formats and vice versa. It will have API functionality. Mainly this service can utilized by the any size of business customer and doesn't require much investment in this application.
Here I am providing some sort of soultion in high level with example of processing
of ZUGFeRD (Germany) e-invoice format
Here is the ### Unified Format (common format) of E-Invoice
```json
{
"invoice": {
"invoiceNumber": "string",
"invoiceDate": "string",
"supplier": {
"name": "string",
"address": "string",
"taxIdentifier": "string",
"country": "string"
},
"buyer": {
"name": "string",
"address": "string",
"taxIdentifier": "string",
"country": "string"
},
"lineItems": [
{
"description": "string",
"quantity": "number",
"unitPrice": "number",
"totalAmount": "number",
"taxes": [
{
"type": "string",
"rate": "number",
"amount": "number"
}
]
}
],
"totalAmount": "number",
"totalTaxes": "number",
"digitalSignature": "string",
"extensions": {
"countrySpecificField1": "string",
"countrySpecificField2": "string"
}
}
}
```
Here is the ### ZUGFeRD Sample Invoice (Simplified XML)
```xml
Here is the mapping between Unified E-Invoice Format and ZUGFeRD (Germany) E-Invoice format
| | ZUGFeRD Field | |Unified Format Field | |
|---|---|
| || `<ram:ID>` | |`invoice.invoiceNumber` | |
| || `<ram:IssueDateTime><udt:DateTimeString>` | |`invoice.invoiceDate` | |
| || `<ram:SellerTradeParty><ram:Name>` | |`invoice.supplier.name` | |
| || `<ram:SellerTradeParty><ram:PostalTradeAddress><ram:LineOne>, <ram:CityName>, <ram:PostcodeCode>, <ram:CountryID>` | |`invoice.supplier.address` | |
| || `<ram:SellerTradeParty><ram:SpecifiedTaxRegistration><ram:ID>` | |`invoice.supplier.taxIdentifier` | |
| || `<ram:SellerTradeParty><ram:PostalTradeAddress><ram:CountryID>` | |`invoice.supplier.country` | |
| || `<ram:BuyerTradeParty><ram:Name>` | |`invoice.buyer.name` | |
| || `<ram:BuyerTradeParty><ram:PostalTradeAddress><ram:LineOne>, <ram:CityName>, <ram:PostcodeCode>, <ram:CountryID>` | |`invoice.buyer.address` | |
| || `<ram:BuyerTradeParty><ram:SpecifiedTaxRegistration><ram:ID>` | |`invoice.buyer.taxIdentifier` | |
| || `<ram:BuyerTradeParty><ram:PostalTradeAddress><ram:CountryID>` | |`invoice.buyer.country` | |
| || `<ram:IncludedSupplyChainTradeLineItem><ram:SpecifiedTradeProduct><ram:Name>` | |`invoice.lineItems[n].description` | |
| || `<ram:IncludedSupplyChainTradeLineItem><ram:SpecifiedLineTradeDelivery><ram:BilledQuantity>` | |`invoice.lineItems[n].quantity` | |
| || `<ram:IncludedSupplyChainTradeLineItem><ram:SpecifiedLineTradeAgreement><ram:GrossPriceProductTradePrice><ram:ChargeAmount>` | |`invoice.lineItems[n].unitPrice` | |
| || `<ram:IncludedSupplyChainTradeLineItem><ram:SpecifiedLineTradeSettlement><ram:SpecifiedTradeSettlementLineMonetarySummation><ram:LineTotalAmount>` | |`invoice.lineItems[n].totalAmount` | |
| || `<ram:IncludedSupplyChainTradeLineItem><ram:SpecifiedLineTradeSettlement><ram:ApplicableTradeTax><ram:TypeCode>` | |`invoice.lineItems[n].taxes[m].type` | |
| || `<ram:IncludedSupplyChainTradeLineItem><ram:SpecifiedLineTradeSettlement><ram:ApplicableTradeTax><ram:RateApplicablePercent>` | |`invoice.lineItems[n].taxes[m].rate` | |
| || `<ram:IncludedSupplyChainTradeLineItem><ram:SpecifiedLineTradeSettlement><ram:ApplicableTradeTax><ram:CalculatedAmount>` | |`invoice.lineItems[n].taxes[m].amount` | |
| || `<ram:SpecifiedTradeSettlementMonetarySummation><ram:GrandTotalAmount>` | |`invoice.totalAmount` | |
| || `<ram:SpecifiedTradeSettlementMonetarySummation><ram:TaxTotalAmount>` | |`invoice.totalTaxes` | |
Here is the output of E-Invoice in Unified Format from ZUGFeRD format
```json
{
"invoice": {
"invoiceNumber": "INV001",
"invoiceDate": "2023-07-19",
"supplier": {
"name": "Supplier Name",
"address": "123 Supplier St, Supplier City, 12345",
"taxIdentifier": "DE123456789",
"country": "DE"
},
"buyer": {
"name": "Buyer Name",
"address": "456 Buyer Ave, Buyer City, 67890",
"taxIdentifier": "DE987654321",
"country": "DE"
},
"lineItems": [
{
"description": "Product Description",
"quantity": 10,
"unitPrice": 10.00,
"totalAmount": 100.00,
"tax
es": [
{
"type": "VAT",
"rate": 10,
"amount": 10.00
}
]
}
],
"totalAmount": 110.00,
"totalTaxes": 10.00,
"digitalSignature": "",
"extensions": {}
}
}
```Above mentioned output document will be pushed / send to the buyers in elctronic form.
Tuesday, July 2, 2024
How Open Banking is Transforming Fintech Innovations
In the rapidly evolving landscape of financial technology, open banking stands out as a transformative movement, redefining how data is shared and utilized across the financial ecosystem. By leveraging APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) to securely share financial information between institutions and third-party providers, open banking has paved the way for a new era of competition and innovation. This paradigm shift not only fosters a more dynamic and inclusive financial market but also highlights the critical importance of security in managing and protecting sensitive financial data. The article delves into an overview of open banking, elaborating on its advantages such as enhanced competition, increased innovation, and improved customer experiences.
Open Banking Overview
Open banking, also referred to as "open bank data," is a practice that revolutionizes the traditional banking system by providing third-party financial service providers with open access to consumer banking, transaction, and other financial data from banks and non-bank financial institutions through application programming interfaces (APIs). This system enables the networking of accounts and data across institutions, which can be utilized by consumers, financial institutions, and third-party service providers. The core of open banking lies in its ability to allow access and control of consumer banking and financial accounts through third-party applications. This access is typically granted by the consumers themselves, who must provide consent, such as agreeing to terms of service on an application. The APIs used in open banking facilitate a variety of services, including comparing financial products, aggregating data for marketing purposes, or conducting transactions on behalf of the consumer. One of the pivotal benefits of open banking is its potential to reshape the competitive landscape of the banking industry. By promoting a network-based rather than a centralized system, open banking enhances the ability of financial services customers to securely share their financial data with other institutions. For instance, open banking APIs can simplify the process of switching bank services or identifying the most suitable financial products for consumers, thereby fostering both innovation and competition. However, open banking also introduces significant challenges, particularly in terms of security and privacy. The wide sharing of consumer data increases the risks of data breaches and financial fraud. It is crucial for open banking frameworks to implement robust security measures to protect consumer information and ensure the integrity of financial transactions. Globally, the implementation of open banking varies. Regions like the UK and European Economic Area have adopted a regulatory approach, mandating banks to develop open banking frameworks. In contrast, countries like the US, Singapore, and India have taken a market-led approach, which may lead to faster innovation but also inconsistencies in standards and practices. In conclusion, open banking represents a transformative development in the financial services sector, offering significant benefits in terms of innovation and consumer choice, but also requiring careful management of the associated risks.
Advantages of Open Banking
Convenience and Efficiency Open banking significantly enhances the convenience and efficiency of financial management. By allowing the aggregation of account information into a single dashboard, open banking enables customers to view all their financial data in one place, simplifying the way they interact with their finances. Additionally, open banking can expedite the approval processes for financial products such as mortgages, reducing the need for extensive paperwork and saving valuable time. This streamlined approach not only improves the user experience but also accelerates decision-making and financial transactions, benefiting both consumers and businesses.
Personalization of Services
The personalization of financial services is a key advantage of open banking. Through the use of APIs, financial service providers can access a wealth of customer data, enabling them to offer tailored financial products and advice. This can include everything from personalized budgeting tools and investment advice to custom loan offers that match the user's financial profile. For businesses, open banking facilitates the delivery of specialized financial services such as targeted lending solutions or treasury services, enhancing customer satisfaction and engagement.
Security and Trust
Open banking also offers improved security and builds trust among users. By implementing strong customer authentication protocols and ensuring that financial transactions go through rigorous security checks, open banking reduces the risk of fraud and unauthorized access. Customers have granular control over their data, deciding who can access their information and to what extent, which enhances their confidence in using open banking platforms. Moreover, the use of blockchain technology in open banking provides an additional layer of security, making data exchanges virtually tamper-proof. This robust security framework not only protects consumers but also fosters trust in the open banking ecosystem, encouraging more users to embrace these innovative financial services.
Challenges and Risks Regulation and Compliance
Navigating the complex landscape of regulatory requirements presents a significant challenge in open banking. Financial institutions and third-party providers must adhere to diverse data protection, consumer rights, and anti-money laundering regulations that vary across jurisdictions . This complexity can hinder the consistency and speed of open banking adoption, as entities must ensure compliance with evolving standards to avoid legal repercussions.
Security Concerns
The sharing of sensitive financial data inherent in open banking increases the risk of unauthorized access, data breaches, and misuse of personal information. To mitigate these risks, robust security measures including encryption, authentication, and intrusion detection systems are essential. Additionally, the integration of third-party services exacerbates security concerns, as these entities often become new targets for cyber-attacks, potentially increasing the vulnerability of the entire banking ecosystem.
Consumer Trust
Building and maintaining consumer trust is crucial for the success of open banking. Transparent communication and explicit consent for data sharing are fundamental to assuring customers of their data's security. However, challenges arise as consumers may not fully understand or trust the open banking framework, especially in regions where it is a relatively new concept. Educating consumers about the benefits and risks of open banking is vital to fostering acceptance and promoting its safe use. Future of Open Banking The future of open banking is poised for substantial growth and transformation, driven by technological advancements and increasing global adoption. The open banking market is expected to expand significantly, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 46.94%, reaching an estimated value of USD 552,620.35 million by 2028 .
Emerging Trends
Several emerging trends are shaping the future of open banking. The integration of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and big data analytics is anticipated to enhance the functionality and scope of open banking services. These technologies enable the personalization of financial services, offering consumers tailored financial advice, automated savings plans, and customized investment recommendations. Additionally, the expansion of the open banking ecosystem and the focus on customer-centric solutions are expected to drive innovation and improve the user experience. Blockchain technology is also emerging as a key player in the open banking landscape, providing enhanced security and transparency for financial transactions . The adoption of standardized APIs across the industry is improving interoperability between financial institutions and fintech firms, further facilitating the seamless exchange of financial data.
Potential Market Growth
The open banking market is experiencing robust growth across various regions. In Europe, the adoption of open banking solutions is accelerating, positioning the region at the forefront of the open banking movement. This growth is supported by the increasing investment in advanced technologies and a strong regulatory framework that promotes innovation and competition. In North America, the market is driven by consumer demand for digital financial services, encouraging banks to invest in open banking APIs and collaborate with fintech firms . The Asia Pacific region is witnessing the fastest growth, driven by a surge in digital payment services and a growing awareness of the benefits of open banking . The Middle East and Africa are also seeing significant growth, with regulatory frameworks supporting the adoption of open banking. The future of open banking represents a paradigm shift in the financial services industry, offering promising opportunities for innovation, enhanced security, and improved customer experiences. As the sector continues to evolve, it will likely play a crucial role in shaping the landscape of global financial services.
Conclusion
Throughout this exploration of open banking, we've delved into its significant capacity to revolutionize the financial landscape by enabling enhanced data sharing and fostering innovation. We've recounted the essential benefits that open banking presents, such as personalized financial services, increased efficiency, and heightened security, alongside acknowledging the hurdles it faces, including regulatory compliance, security concerns, and the vital need for consumer trust. By examining these facets, the article has underscored open banking's pivotal role in driving technological advancements within the fintech industry, showcasing its potential to radically transform consumer experiences and the competitive dynamics among financial providers. As we gaze into the future, the trajectory of open banking appears inherently linked with the continuous evolution of technology and regulatory frameworks, suggesting a landscape ripe with opportunities for both consumers and businesses. The anticipated expansion and integration of emerging technologies, like AI and blockchain, with open banking platforms, promise to further refine and secure the financial services ecosystem, paving the way for a more interconnected and efficient market. Thus, the journey of open banking, while replete with challenges, stands as a beacon of innovation, with its unfolding story poised to redefine the essence of financial services in an increasingly digital world.
FAQs
1. How is fintech reshaping the banking industry? Fintech companies are revolutionizing the banking sector by significantly improving customer experiences. These companies are known for their speed, affordability, efficiency, and enhanced security compared to traditional banking institutions. 2. What does the future hold for Open Banking? The future of Open Banking looks very promising, with expectations for its growth and adoption to continue rising. According to a Forrester report, the number of Open Banking users in Europe is projected to double by the year 2027. 3. What are the advantages of using Open Banking? Open Banking offers numerous benefits, including: Access to a broader array of financial services. Improved personalization and customer experience in banking. Greater control and enhanced security over one's financial data. Promotion of innovation and competition within the banking sector. Better account management. Enhanced budget management and financial analysis capabilities. Easier and simplified payment and transfer processes. 4. In what ways will fintech services improve the banking experience? Fintech companies utilize data analytics and artificial intelligence to provide personalized financial services. These tailored services meet individual needs and preferences, significantly enhancing the overall customer experience in banking.
References
[1] - https://www.investopedia.com/terms/o/open-banking.asp
[2] - https://paymentsconsulting.com/open-banking-five-principles-for-success/
[3] - https://www.mastercard.com/news/perspectives/2022/open-banking-101/
[4] - https://humansofglobe.com/unlocks-the-future-of-personalized-finance-with-open-banking/
[5] - https://www.sydle.com/blog/open-banking-65030cf8697d3e430a055739
[6] - https://stripe.com/resources/more/open-banking-explained
[7] - https://gocardless.com/guides/posts/what-are-the-benefits-of-open-banking/
[8] - https://www.ey.com/en_ca/banking-capital-markets/building-customer-trust-in-open-banking-through-security-transformation
[9] - https://www.financemagnates.com/fintech/payments/overcoming-security-and-privacy-concerns-in-open-banking/
[10] - https://www.getfocal.ai/knowledgebase/what-is-open-banking
[11] - https://seon.io/resources/open-banking-risk-and-fraud/
[12] - https://www.openbankproject.com/blog/open-banking-10-challenges-for-regulators/
[13] - https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/open-banking-market-future-growth-developments-6edqf/
[14] - https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/Market-Reports/open-banking-solutions-market-160940134.html
[15] - https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/open-banking-systems-market
[16] - https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/ResearchInsight/emerging-trends-in-open-banking-solutions-market.asp
[17] - https://www.powens.com/blog/9-open-banking-trends-predicted-to-dominate-in-2023/
Comparison of the latest IBM Sterling Integrator map editor vs. IBM Transformation Extender (ITX) map editors
Here’s a comparison of the latest IBM Sterling Integrator map editor vs. IBM Transformation Extender (ITX) map editor from a data-mapping p...
-
Inbound Flow: 1) The inbound, EDI data needs to be collected. 2) The collected data should be De-enveloped (removing the headers) to get t...
-
Sterling Integrator Administaration Related Interview Questions : ...
-
Encoding Conversion (From ISO8859_1 / ISO-8859_1 / ISO_8859_1 to UTF8 and vice versa) There is one service called “Encoding Conversion” in...

.png)