Thursday, January 8, 2026
Check Your IPv4 and IPv6 of Public IP of your system
Thursday, May 1, 2025
Automate Resume Screening with TAOne.AI | Fast & Smart Talent Filtering Process 500+ Resumes in Hour
Thursday, January 2, 2025
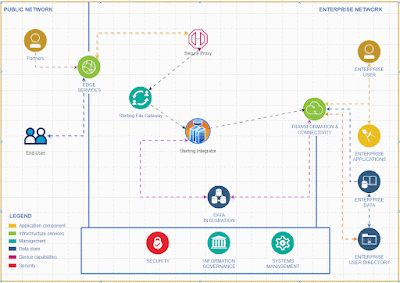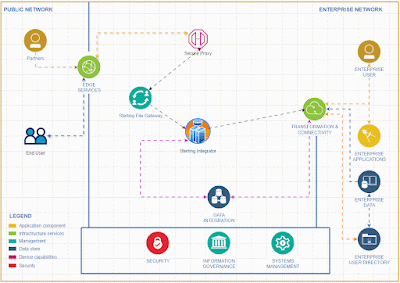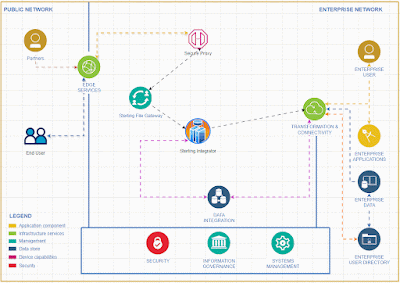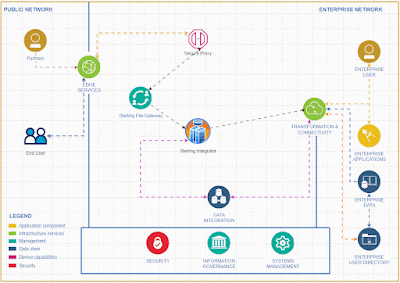
Implementing EDI Integration Using Microsoft Azure Logic Apps
# Implementing EDI Integration Using Microsoft Azure Logic Apps
This comprehensive guide provides a step-by-step approach to implementing EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) integration using Microsoft Azure Logic Apps. Azure Logic Apps is a cloud-based service designed to help automate workflows and integrate EDI transactions seamlessly with your systems and trading partners.
---
## **Step 1: Prerequisites** Before starting the implementation, ensure you have the following:
1. **Azure Subscription**: - Sign up for an Azure account if you don’t already have one. - Access the Azure Portal.
2. **Trading Partner EDI Specifications**: - Obtain the EDI implementation guide for the documents you will exchange (e.g., EDI 810, EDI 850).
3. **Existing Systems**: - Identify the systems (e.g., ERP, CRM) that will integrate with EDI workflows.
4. **Data Format**: - Define the data format (e.g., X12, EDIFACT, XML) based on trading partner requirements.
---
## **Step 2: Create a Logic App** 1. **Log in to Azure Portal**: - Navigate to the Azure portal and search for "Logic Apps."
2. **Create a New Logic App**: - Click "Create" and provide the following details: - **Resource Group**: Create or select an existing resource group. - **Name**: Name your Logic App (e.g., `EDI_Integration_Workflow`). - **Region**: Select the appropriate region for hosting.
3. **Open Logic App Designer**: - Open the Logic App in Designer mode to start building your workflow.
---
## **Step 3: Add EDI Integration Connector** Azure provides built-in connectors for EDI transactions, such as AS2, X12, and EDIFACT.
### **For X12 EDI** 1. **Set Up an Integration Account**: - Navigate to "Integration Accounts" in the Azure portal. - Create an Integration Account and link it to your Logic App.
2. **Upload Partner Agreements**: - Define trading partners and upload their details (e.g., X12 schemas, certificates, and agreements) into the Integration Account. - Add: - **Schemas**: Import X12 schema files for the EDI document types you are processing. - **Partners**: Add trading partner details (identifiers, roles, and agreements). - **Agreements**: Configure inbound and outbound agreements specifying EDI protocols and settings.
3. **Configure X12 Connector**: - In the Logic App Designer, search for "EDI X12" and add the X12 connector. - Choose "Receive X12 Message" or "Send X12 Message" based on the workflow.
---
## **Step 4: Design the Workflow**
### **Inbound EDI Workflow** 1. **Receive EDI Document**: - Add a trigger to start the Logic App, such as "When a file is added to Azure Blob Storage" or "Receive AS2 message."
2. **Decode EDI Message**: - Use the "EDI Decode" action to validate and parse the received EDI document. - Map the EDI segments to readable data (e.g., JSON, XML).
3. **Transform Data**: - Add a "Transform XML" action to convert the EDI message into the desired format for your system. - Use a predefined map or create one using Azure’s mapping tools.
4. **Send Data to System**: - Add an action to send the transformed data to your internal system (e.g., SQL Database, Dynamics 365).
### **Outbound EDI Workflow** 1. **Receive Data from System**: - Add a trigger to listen for new data in your system (e.g., "When an item is created in SQL Database").
2. **Transform Data**: - Use the "Transform XML" action to convert internal data into the required EDI format.
3. **Encode EDI Message**: - Use the "EDI Encode" action to package the data into an X12-compliant EDI document.
4. **Send EDI Document**: - Add an action to send the EDI document to the trading partner via AS2, FTP, or another protocol.
---
## **Step 5: Test the Integration** 1. **Enable Logging**: - Use Azure Monitor or Application Insights to track the execution of your Logic App.
2. **Perform Test Runs**: - Simulate inbound and outbound transactions using test data. - Verify that the EDI documents are generated, validated, and transmitted correctly.
3. **Fix Errors**: - Debug any errors using the Logic App’s run history and logs.
---
## **Step 6: Go Live** 1. **Deploy the Logic App**: - Ensure all configurations are in place and move the Logic App to production.
2. **Monitor Live Transactions**: - Use Azure’s monitoring tools to ensure smooth operation and address any issues promptly.
---
## **Step 7: Maintain and Optimize** 1. **Periodic Reviews**: - Review workflows to ensure compliance with updated trading partner requirements.
2. **Optimize Performance**: - Monitor latency and throughput, and adjust Logic App triggers and actions as needed.
3. **Add New Partners**: - Scale your solution by adding new trading partners or EDI document types.
---
By following this detailed roadmap for implementing EDI integration using Azure Logic Apps, you can streamline your business processes, ensure compliance with trading partner requirements, and achieve efficient and reliable electronic data exchange.
Monday, October 14, 2024
Introducing a rate limiter feature in IBM Sterling Integrator allows for comprehensive API functionality without the need to invest in additional API tools.
To activate and integrate the rate limiter feature in Sterling Integrator for comprehensive API functionality, follow these steps.To effectively deliver a service, it's essential to create a system that accepts input from clients and returns the appropriate output based on that input.
When we offer this service, it's important to pinpoint the client's IP address for any requests originating from outside our network.
To achieve the capability of identifying the client IP address within Sterling Integrator, we should adhere to the following steps.
To activate the Client IP feature, follow these steps: First, include the property client_ip_correlation_enabled=false in the jdbc.properties_platform_ifcbase_ext.in file.
Next, execute ./setupfiles.sh.
This feature captures the IP address of the client that initiates the request.
Certain clients require this functionality to comply with regulatory standards.
Before you enable the Client IP feature, ensure that your firewall is configured to permit the IP address to pass through the Sterling External Authentication Server.
We will now verify the available rate limit for the customer associated with the given IP address.
As developers, we will save this information in our database. Each time a request is received, we will assess the rate limit for that partner.
If the request falls within the allowed rate limit, it will be forwarded to the appropriate API service.
Additionally, we can implement another check to monitor the number of requests made by the partner within a defined time frame. For instance, we could allocate a limit of 1,000 requests per hour for a specific partner based on their IP address.
To put this into action, we will track the number of requests made by the partner.
If any conditions fail, we will provide the relevant error code and description to the partner. They will need to rectify the issue by upgrading their subscription with the service provider.
When we integrate this functionality into Sterling Integrator, we can incorporate rate limiting within a generic process. If the result is positive, the request will then be directed to the appropriate API service business process.
I recommend implementing API capabilities in Sterling Integrator rather than using specific API tools for small and medium business who is already using Sterling Integrator for their EDI integrations .Given the business capacity, Sterling Integrator can effectively expose API services to the external world. It offers robust error handling features and a clear understanding of error codes, making it particularly suitable for small and medium-sized businesses.
The Sterling Integrator Server offers enhanced functionality, equipped with a wider array of services and adapters, allowing us to implement simple functions without the need for coding.
Tracking requests and generating reports is a breeze with the Sterling File Gateway.
While this tool primarily focuses on managing EDI-based transactions, it can also be effectively utilized for API service implementations.
There is a wealth of Sterling technical resources available in the market.
One important consideration when using Sterling Integrator as an API endpoint is that it only supports XML-based transactions and requests, excluding JSON format. To address this limitation, we can create an alternative solution by leveraging the Java Task Service to develop a Java program that formats JSON.
1. One minor limitation of the API toolscurrently on the market is that implementing any functionality requires coding in a language chosen by the organization or developer.
Maintaining this code can also pose challenges within the organization.
Should there be any updates or changes to the service in the future, it may necessitate hiring new personnel with expertise in the original programming language or rewriting the functionality in a different language altogether.
Additionally, as a centralized access point, an API serves as a gateway that can attract the attention of hackers. If an API is breached, it can expose all connected applications and systems to potential threats.
Monday, September 30, 2024
Workato Automation Tool and main capabilities when compare to other iPAAS tools like Dell Boomi
Dears
Good Day
Hope you are doing good.
I would like to share my recent achievement: yesterday, I successfully completed the Workato Automation Pro I tool certification as part of my efforts to enhance my skill set.
Some brief introduction about Workato Automation Tool ,
Workato is an automation tool that helps businesses connect different apps and systems without needing a lot of coding. It allows you to create workflows, called "recipes," that automate tasks like sending data from one app to another or triggering actions based on events. For example, it can automatically update a spreadsheet when a new order is placed or send an email when a project status changes. Workato works with many popular apps like Salesforce, Slack, and QuickBooks, making it easier to streamline work processes and save time on repetitive tasks.
This tool boasts enhanced security features compared to another iPaaS solution, Boomi. Additionally, it offers a unique capability to retain the failed steps of a process during unexpected system failures, automatically resuming process executions once the system restarts. This means there's no need for us to manually check whether we need to reprocess any failed processes.
#integration #EDI #B2B #Workato #Salesforce #Banking #Finance #IToperations #automation #QuickBooks #insurance #Retail #API #AI #IBM #boomi #ipaas #saas
LinkedIn Post Link: [Insert your LinkedIn post link here]
Workato Automation Tool brief description about Workato automation tool in layman wordsWorkato is an automation tool that helps businesses connect different apps and systems without needing a lot of coding. It allows you to create workflows, called "recipes," that automate tasks like sending data from one app to another or triggering actions based on events. For example, it can automatically update a spreadsheet when a new order is placed or send an email when a project status changes. Workato works with many popular apps like Salesforce, Slack, and QuickBooks, making it easier to streamline work processes and save time on repetitive tasks.
Write a BOT Application using JAVA to take the blog posts from Blogger website login and post that blog post in the Twitter channel on scheduled base
To create a bot application in Java that retrieves blog posts from Blogger, logs in, and posts those blog posts to a Twitter channel on a scheduled basis, you can follow these steps:
### Overview
1. **Fetch blog posts from Blogger**: Use the Google Blogger API to retrieve blog posts.
2. **Post on Twitter**: Use the Twitter API to post the content.
3. **Schedule the task**: Use a scheduler like `java.util.Timer` or Spring Scheduler to post the blogs at regular intervals.
4. **OAuth Authentication**: Handle OAuth authentication for both Blogger and Twitter.
### Dependencies
To get started, you'll need the following dependencies:
1. **Google Blogger API client**: To interact with Blogger.
2. **Twitter API client**: Use Twitter4J for Twitter API integration.
3. **Scheduler**: Use `java.util.Timer` or Spring for scheduling.
4. **OAuth Libraries**: You’ll need OAuth libraries for both Google and Twitter.
Here’s an example with these steps using Java:
### 1. Add Maven Dependencies
First, add the necessary dependencies to your `pom.xml`:
```xml
You'll need to configure Google OAuth2 to fetch Blogger posts. You can get the credentials from the [Google Developer Console](https://console.developers.google.com/).
Here’s the code to authenticate and fetch the posts:
```java
import com.google.api.services.blogger.Blogger;
import com.google.api.services.blogger.model.Post;
import com.google.api.services.blogger.model.PostList;
import com.google.api.client.googleapis.auth.oauth2.GoogleCredential;
import com.google.api.client.http.javanet.NetHttpTransport;
import com.google.api.client.json.JsonFactory;
import com.google.api.client.json.jackson2.JacksonFactory;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.List;
public class BloggerAPIService {
private static final String APPLICATION_NAME = "BloggerPostBot";
private static final String BLOG_ID = "your-blog-id"; // Replace with your blog ID
private static Blogger bloggerService;
public static Blogger getBloggerService() throws IOException {
if (bloggerService == null) {
GoogleCredential credential = GoogleCredential
.fromStream(new FileInputStream("path/to/your/client_secret.json"))
.createScoped(Collections.singleton("https://www.googleapis.com/auth/blogger"));
bloggerService = new Blogger.Builder(new NetHttpTransport(), JacksonFactory.getDefaultInstance(), credential)
.setApplicationName(APPLICATION_NAME)
.build();
}
return bloggerService;
}
public static List
Blogger.Posts.List request = getBloggerService().posts().list(BLOG_ID);
PostList posts = request.execute();
return posts.getItems();
}
}
```
### 3. Post Blog Content on Twitter
You will need to configure Twitter OAuth keys (API Key, API Secret Key, Access Token, Access Token Secret) on the [Twitter Developer Platform](https://developer.twitter.com/).
Here’s how you can post the content using Twitter4J:
```java
import twitter4j.Twitter;
import twitter4j.TwitterException;
import twitter4j.TwitterFactory;
import twitter4j.conf.ConfigurationBuilder;
public class TwitterBot {
private static Twitter twitter;
public static Twitter getTwitterInstance() {
if (twitter == null) {
ConfigurationBuilder cb = new ConfigurationBuilder();
cb.setDebugEnabled(true)
.setOAuthConsumerKey("your-consumer-key")
.setOAuthConsumerSecret("your-consumer-secret")
.setOAuthAccessToken("your-access-token")
.setOAuthAccessTokenSecret("your-access-token-secret");
TwitterFactory tf = new TwitterFactory(cb.build());
twitter = tf.getInstance();
}
return twitter;
}
public static void postTweet(String content) {
try {
getTwitterInstance().updateStatus(content);
System.out.println("Successfully posted: " + content);
} catch (TwitterException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
```
### 4. Schedule the Posting
You can use `java.util.Timer` or Spring’s `@Scheduled` to post blogs at regular intervals.
Here’s an example using Spring’s Scheduler:
```java
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Scheduled;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.List;
@Component
public class BloggerTwitterScheduler {
@Scheduled(cron = "0 0 * * * *") // Every hour
public void postBlogToTwitter() {
try {
List
for (Post post : blogPosts) {
String content = post.getTitle() + "\n" + post.getUrl();
TwitterBot.postTweet(content);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
```
### 5. Main Class
```java
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
@SpringBootApplication
@ComponentScan(basePackages = {"your.package.name"})
public class BloggerTwitterBotApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(BloggerTwitterBotApplication.class, args);
}
}
```
### 6. Application Properties
Add your application properties in `application.properties`:
```properties
spring.main.web-application-type=none
```
### 7. Running the Application
1. Obtain the necessary OAuth credentials for Google Blogger and Twitter.
2. Run the application, and it will fetch the blog posts and post them on Twitter on a scheduled basis.
---
This is a simplified version. You may want to add error handling, logging, and edge cases (e.g., duplicate posts, scheduling intervals).
LinkedIn Post Link: [Insert your LinkedIn post link here]
Tuesday, September 17, 2024
Online Cross Browser Testing module , Test your website with any list browsers and OS favors and get instant feedback about your Website
Online Cross-Browser Testing
Select browsers and OS flavors to run your website tests.
Cross-browser testing is the process of testing a website or web application across multiple browsers to ensure consistent functionality, design, and user experience. Different browsers (such as Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge) may interpret web code (HTML, CSS, JavaScript) differently, which can lead to variations in how a site is displayed or behaves.
The purpose of cross-browser testing is to identify these inconsistencies and address them, ensuring that the web application works as intended for all users, regardless of which browser they are using. It typically involves:
- **Checking for Layout Differences**: Ensuring that the design and user interface (UI) look consistent across different browsers.
- **Verifying Functionality**: Ensuring that key functions (e.g., buttons, forms, navigation) work properly in each browser.
- **Testing JavaScript/DOM**: Ensuring that interactive elements and scripts behave consistently.
- **Performance Testing**: Checking load times and performance differences across browsers.
- **Device Compatibility**: Ensuring that the website works properly on both desktop and mobile versions of browsers.
Sunday, August 25, 2024
To set up sales reports using SPS Commerce for EDI, you need to ensure proper configuration of your EDI processes and reports to accurately reflect sales data
### 1. **Data Integration Setup**
- **Identify Data Flow**: Determine what sales data is needed for reporting (e.g., purchase orders, invoices, inventory updates). Key documents include EDI 850 (Purchase Order), EDI 810 (Invoice), and EDI 867 (Product Transfer and Resale Report).
- **Establish Communication Channels**:
- Choose the communication method that works with your partners, such as **AS2, FTP, or VAN** (Value-Added Network).
- Ensure that your system is capable of sending and receiving EDI transactions. If you're using an ERP system like SAP, Oracle, or NetSuite, ensure it’s integrated with **SPS Commerce**.
- **Test Connectivity**: Perform end-to-end tests with trading partners to ensure EDI transactions are being sent and received properly. Use SPS Commerce’s testing tools to validate connectivity and document formats.
### 2. **Mapping Sales Data**
- **Identify Document Types**: For sales reporting, focus on key EDI document types:
- **EDI 850**: Purchase Order - Helps track orders placed by customers.
- **EDI 810**: Invoice - Details invoiced amounts and products sold.
- **EDI 856**: Advance Ship Notice - Helps track the shipments of goods.
- **EDI 867**: Product Transfer and Resale Report - Specific for reporting detailed product sales data back to the supplier.
- **EDI 846**: Inventory Inquiry/Advice - Track inventory levels for accurate sales reporting.
- **Data Mapping**: Work with your IT or EDI team to create mappings between the data in these documents and your internal business systems. Mapping ensures that each EDI field is correctly interpreted by your ERP, accounting, or CRM systems. SPS Commerce typically provides a mapping tool for this.
- **Customization**: You may need to customize mappings to reflect specific customer or supplier requirements, such as custom fields or non-standard data elements. Review your trading partner agreements for details.
### 3. **Report Configuration**
- **Define Reporting Requirements**: Define the scope of your sales reports, including the specific data points to track. For example:
- **Total Sales Volume**: Track the total amount of sales over a given period.
- **Sales by Region**: Break down sales by geographic region, if applicable.
- **Product Performance**: Track sales by product type or category.
- **Customer Segmentation**: Identify which customers are purchasing the most products.
- **Report Customization**:
- SPS Commerce’s platform includes reporting tools, often integrated with an **Analytics** module. Use these tools to create custom sales reports that pull data from multiple EDI documents.
- Choose report formats (e.g., Excel, PDF, or CSV) based on your business needs.
- Work with SPS Commerce’s support team to set up custom fields or filters that might be unique to your business.
- **Set Report Parameters**:
- Configure parameters such as time periods (e.g., daily, weekly, or monthly reports) and specific products or regions to track.
- You may also choose to set thresholds or alerts for certain key metrics (e.g., low stock levels or high sales volume).
### 4. **Scheduled and Automated Reports**
- **Set Up Recurring Reports**: Configure SPS Commerce to generate sales reports automatically on a recurring basis. You can set the frequency based on business requirements (e.g., daily, weekly, or monthly).
- **Automated Alerts**: If needed, set up automated notifications when certain thresholds are met (e.g., a sudden spike in sales or low inventory levels). These can help you take immediate action based on the data.
### 5. **Testing and Validation**
- **Run Sample Reports**: Before going live, run a few sample sales reports to ensure the data is accurate and the report format meets your needs. Check for:
- **Data Accuracy**: Ensure the report is correctly pulling sales data from EDI transactions and that no critical data is missing.
- **Report Structure**: Verify that the reports are structured correctly with proper headings, summaries, and filters.
- **Cross-check with Business Systems**: Cross-validate the EDI-generated reports with your ERP or internal systems to ensure consistency across all platforms.
- **Review with Stakeholders**: Share the reports with key stakeholders to get feedback and make any necessary adjustments to the report layout or data points.
### 6. **Live Reporting and Monitoring**
- **Go Live**: Once testing is complete and the reports meet your business requirements, implement them into your live environment.
- **Monitor Reports**: e monitor sales reports to ensure data integrity over time. Address any discrepancies immediately by working with your EDI and IT teams.
- **Adjust as Needed**: Sales reporting needs may evolve, so be prepared to adjust the report parameters or data mappings as your business grows or changes.
### 7. **Ongoing Maintenance**
- **Update Mapping and Configuration**: As trading partners update their EDI requirements or you onboard new ones, update the data mappings and report configurations.
- **New Document Types**: If new EDI documents are introduced or existing ones change (e.g., new fields in the EDI 867 for product resale reports), update your system accordingly.
- **Training**: Keep your team trained on how to interpret and utilize the sales reports generated by SPS Commerce. Also, ensure that your staff is aware of any new reporting capabilities or changes in the reporting process.
### 8. **Advanced Analytics (Optional)**
- If you need more in-depth insights beyond basic sales data, SPS Commerce offers advanced **Analytics** features:
- **Sales Trends Analysis**: Identify long-term sales trends and seasonal patterns.
- **Inventory Management**: Track inventory levels alongside sales data to ensure that stock levels are in line with demand.
- **Forecasting**: Use sales data to forecast future trends and adjust purchasing strategies accordingly.
Sunday, August 4, 2024
JSON to XML and XML to JSON converter in second . Use it for API integrations and Web development projects
Wednesday, July 24, 2024
Saturday, January 20, 2024
What are the steps to follow to integrate VMS with Banks for vendor payment | Amazon | VendorPayments|Walmart|Integration|EDI|B2B|Security
Integrating a vendor management system (VMS) with banks for vendor payment involves several steps to ensure a seamless and secure payment process. Here's a comprehensive overview of the integration process:
Step 1: Define requirements and objectives
Clearly define the objectives of integrating the VMS with banks for vendor payment. Identify the specific payment methods, data exchange formats, and security protocols that need to be supported. This will help in selecting the appropriate integration approach and tools.
Step 2: Select a VMS and bank connectivity solution
Choose a VMS that offers integration capabilities with multiple banks and supports various payment methods. Evaluate the compatibility of the VMS with the bank's payment systems and ensure it meets your specific requirements.
Step 3: Establish data exchange standards
Determine the data exchange standards that will be used for transmitting payment information between the VMS and the bank. Common standards include XML, EDI, and SWIFT. Ensure that both systems can communicate effectively using the chosen standards.
Step 4: Implement data mapping and transformation
Map the data fields in the VMS to the corresponding fields in the bank's payment systems. This may involve data transformation, such as formatting and conversion, to ensure compatibility. Develop data validation rules to ensure data integrity and prevent errors.
Step 5: Configure payment workflows
Define the payment workflows between the VMS and the bank. This includes specifying the authorization process, payment initiation, and reconciliation procedures. Establish clear roles and responsibilities for each step in the workflow.
Step 6: Conduct testing and validation
Perform thorough testing to ensure the integration is functioning as expected. Test various payment scenarios, including single payments, batch payments, and error handling. Validate data accuracy, transaction processing, and communication between the VMS and the bank.
Step 7: Deploy and monitor the integration
Deploy the integrated solution to a production environment and monitor its performance closely. Continuously review and refine the integration to address any issues or optimize the payment process.
Additional considerations for secure integration:
-
Employ strong encryption and authentication mechanisms to protect sensitive payment data.
-
Implement access controls and user authorization to restrict access to payment information based on user roles and permissions
-
Conduct regular security audits and vulnerability assessments to identify and address potential security risks.
-
Follow industry standards and best practices for secure payment processing.
Integrating a vendor management system (VMS) with banks for vendor payment involves several steps to ensure a seamless and secure payment process. Here's a comprehensive overview of the integration process:
Step 1: Define requirements and objectives
Clearly define the objectives of integrating the VMS with banks for vendor payment. Identify the specific payment methods, data exchange formats, and security protocols that need to be supported. This will help in selecting the appropriate integration approach and tools.
Step 2: Select a VMS and bank connectivity solution
Choose a VMS that offers integration capabilities with multiple banks and supports various payment methods. Evaluate the compatibility of the VMS with the bank's payment systems and ensure it meets your specific requirements.
Step 3: Establish data exchange standards
Determine the data exchange standards that will be used for transmitting payment information between the VMS and the bank. Common standards include XML, EDI, and SWIFT. Ensure that both systems can communicate effectively using the chosen standards.
Step 4: Implement data mapping and transformation
Map the data fields in the VMS to the corresponding fields in the bank's payment systems. This may involve data transformation, such as formatting and conversion, to ensure compatibility. Develop data validation rules to ensure data integrity and prevent errors.
Step 5: Configure payment workflows
Define the payment workflows between the VMS and the bank. This includes specifying the authorization process, payment initiation, and reconciliation procedures. Establish clear roles and responsibilities for each step in the workflow.
Step 6: Conduct testing and validation
Perform thorough testing to ensure the integration is functioning as expected. Test various payment scenarios, including single payments, batch payments, and error handling. Validate data accuracy, transaction processing, and communication between the VMS and the bank.
Step 7: Deploy and monitor the integration
Deploy the integrated solution to a production environment and monitor its performance closely. Continuously review and refine the integration to address any issues or optimize the payment process.
Additional considerations for secure integration:
-
Employ strong encryption and authentication mechanisms to protect sensitive payment data.
-
Implement access controls and user authorization to restrict access to payment information based on user roles and permissions
-
Conduct regular security audits and vulnerability assessments to identify and address potential security risks.
-
Follow industry standards and best practices for secure payment processing.
Comparison of the latest IBM Sterling Integrator map editor vs. IBM Transformation Extender (ITX) map editors
Here’s a comparison of the latest IBM Sterling Integrator map editor vs. IBM Transformation Extender (ITX) map editor from a data-mapping p...
-
Inbound Flow: 1) The inbound, EDI data needs to be collected. 2) The collected data should be De-enveloped (removing the headers) to get t...
-
Sterling Integrator Administaration Related Interview Questions : ...
-
Encoding Conversion (From ISO8859_1 / ISO-8859_1 / ISO_8859_1 to UTF8 and vice versa) There is one service called “Encoding Conversion” in...

.png)