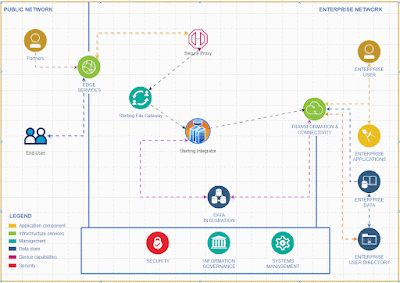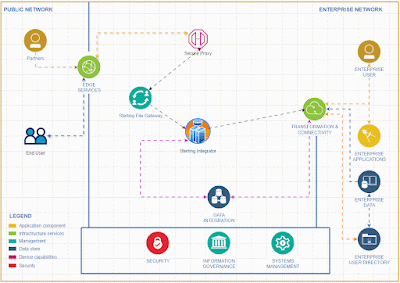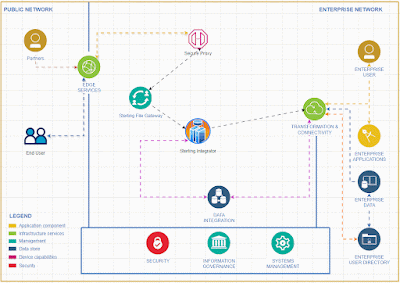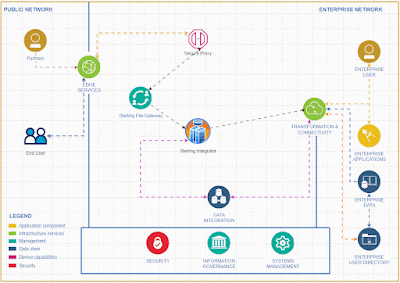
Here's a detailed step-by-step guide on how to generate Workday BIRT (Business Intelligence and Reporting Tool) reports:
---
# **Generating Workday BIRT Reports: Step-by-Step Guide**
## **Introduction to BIRT in Workday** Workday BIRT reports are custom report templates designed using the BIRT tool to create pixel-perfect layouts for operational and transactional reports. These templates can include advanced formatting, custom layouts, and embedded graphics.
---
## **Step 1: Prerequisites**
1. **Access to Workday and Reporting Permissions**: - Ensure you have the necessary permissions in Workday to create and manage reports.
2. **Install BIRT Designer**: - Download and install the Eclipse-based BIRT Designer tool from [Eclipse BIRT](https://www.eclipse.org/birt/).
3. **Familiarity with Workday Report Writer**: - Understand how Workday’s standard report writer works, as BIRT uses custom templates linked to advanced reports.
4. **Technical Knowledge**: - Knowledge of XML data sources, XPath, and design principles for creating report templates.
---
## **Step 2: Design and Build the Advanced Report in Workday**
1. **Create an Advanced Report**: - In Workday, navigate to the “Create Report” task. - Choose **Advanced Report** as the type. - Add the required **Data Sources** and fields based on the report’s purpose. - Filter the data using prompts, conditions, or sorting.
2. **Enable Report for BIRT**: - Go to the advanced report properties and check the option **Enable as BIRT report**.
3. **Generate and Export the XML Output**: - Run the report to generate the XML output. - Save the XML file, which will serve as the data source for your BIRT template.
---
## **Step 3: Develop the BIRT Template**
1. **Launch the BIRT Designer**: - Open the BIRT Designer tool installed on your system.
2. **Create a New Report**: - Start a new report project and name it appropriately.
3. **Import the XML Data Source**: - Add the XML file (exported from Workday) as a data source in BIRT. - Define data sets by mapping fields in the XML file to elements in the report.
4. **Design the Report Layout**: - Use BIRT's drag-and-drop interface to design the report layout. - Include elements such as: - **Tables**: For structured data. - **Charts**: For visual data representation. - **Images and Logos**: For branding. - **Headers and Footers**: For consistent styling.
5. **Add Formatting and Styles**: - Apply custom styles to enhance readability. - Configure fonts, alignments, and color schemes to align with your organizational standards.
6. **Preview the Report**: - Use the preview option to ensure the layout aligns with expectations and displays data correctly.
---
## **Step 4: Upload the BIRT Template to Workday**
1. **Compress the Template**: - Save the BIRT template file as a `.rptdesign` file. - Compress it into a `.zip` file.
2. **Upload the Template**: - In Workday, navigate to the “Maintain BIRT Layout Templates” task. - Upload the `.zip` file and associate it with the appropriate advanced report.
3. **Test the Report**: - Run the advanced report with the uploaded BIRT template to verify the output.
---
## **Step 5: Refine and Optimize**
1. **Review and Adjust**: - Adjust the BIRT template or advanced report settings based on feedback or issues identified during testing.
2. **Performance Optimization**: - Simplify data sources and reduce unnecessary computations to optimize report performance.
3. **Deploy for End Users**: - Share the report with end users, ensuring proper access permissions are set in Workday.
---
## **Step 6: Maintenance and Updates**
1. **Update Templates as Needed**: - Make changes to the BIRT template or advanced report to reflect evolving business requirements.
2. **Monitor Usage**: - Track the usage and performance of the report in Workday to ensure it meets user needs.
3. **Train Users**: - Provide training for end users on interpreting and using the report effectively.
---
This step-by-step process ensures the successful creation and deployment of Workday BIRT reports, enabling high-quality, customized reporting tailored to your organizational needs.